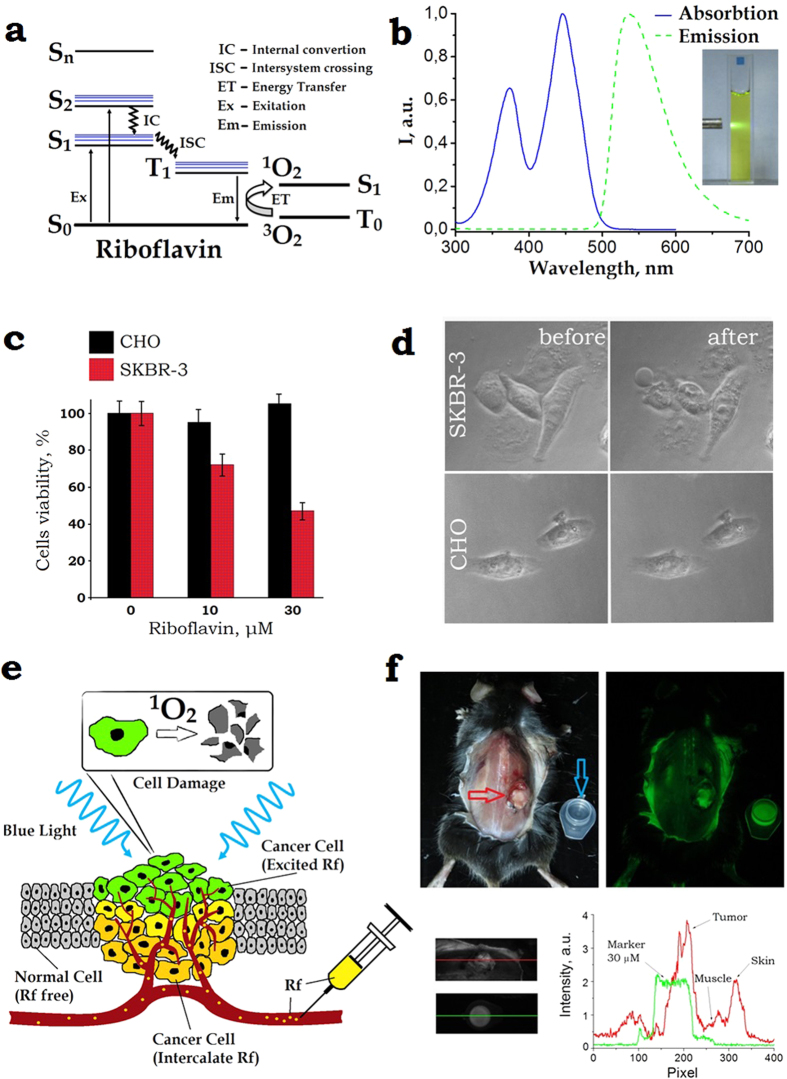
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic diagram of the energy levels of riboflavin. A photon excites Rf from the singlet ground state (S0) to the first excited singlet state (S1) from which it can either decay to the S0 or undergo intersystem crossing to an excited triplet state (T1). Rf in the long-lived T1 state is capable to non-radiatively (collisionally) drive environmental oxygen from its triplet ground state 3O2 to the chemically reactive singlet excited state 1O2. The excitation and emission spectra of Rf are shown in Panel (b). (c) The MTT assay of the cells after incubation with Rf for 90 min followed by 365-nm light exposure at the dose 4.2 J/cm2. SK-BR-3 and CHO cells are marked red and black, respectively. The riboflavin CRf ≈ 30 μM reduced the SKBR-3 cells viability to 47 ± 7%. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD) for three independent experiments. (d) Phase-contrast images of SK-BR-3 and CHO cells treated with 30-μM riboflavin, before (left) and 2-h after (right) 10-min 365-nm light irradiation. Rapture of SK-BR-3 cells membrane was evident (bubbles), whereas the control CHO cells showed no morphological changes. (e) Schematic representation of the Rf-aided photodynamic treatment of superficial layers of targeted cancer cells shown as polymorphic yellow/green-coloured cells embedded into a layer of monomorphic grey-coloured normal cells. Buffer solution of Rf is injected into the tumour interstitium. 1O2 generated in the superficial cancer cell layer (green-coloured) exposed to UV-blue light induce phototoxicity. (f) Top row: left and right panels, post mortem bright-field and epi-luminescent images of BDF1 mice with a Lewis lung carcinoma tumour grafted on the dorsal side (marked by a red arrow), respectively. A plastic cuvette filled with CRf ≈ 30 μM is shown besides the animal (marked by a blue arrow). The epi-luminescent image was acquired under 450-nm excitation; fluorescence detection spectral band was 500–570 nm. Bottom row: bright-field zoomed images of the grafted tumour and cuvette and its fluorescence signal intensity profiles.