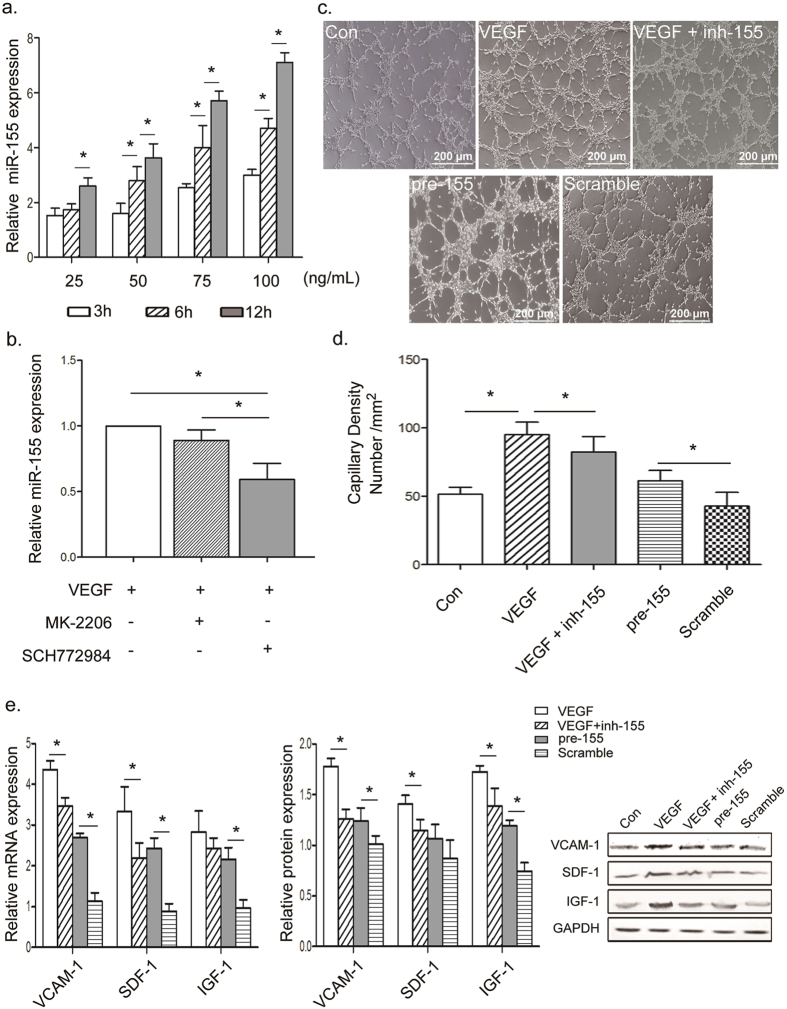
Figure 4. Prolonged VEGF stimulation increased miR-155 by activating the ERK signaling pathway.
(a) miR-155 expression was regulated by VEGF in a time- and dose-dependent manner. (b) After stimulation with 50 ng/mL VEGF for 12 h, miR-155 significantly decreased in the group treated with ERK inhibitor compared with those treated with AKT inhibitor. That indicated that VEGF modulated miR-155 via the ERK signaling pathway. (c,d) Representative photomicrograph and quantification of microtubule formation, depicting effects of VEGF and miR-155 in HUVECs. Angiogenic function of HUVECs was proved to be positively correlated miR-155. Scale bars = 200 μm. (e,f) qPCR and Western blot analysis for the expression of VCAM-1, SDF-1 and IGF-1 in VEGF or pre-155 treatment groups in HUVECs. Pre-155 alone was found to render levels of proangiogenic cytokines, while inh-155 partially reversed VEGF-induced angiogenesis factors. All data are means ± SD. *P < 0.05.