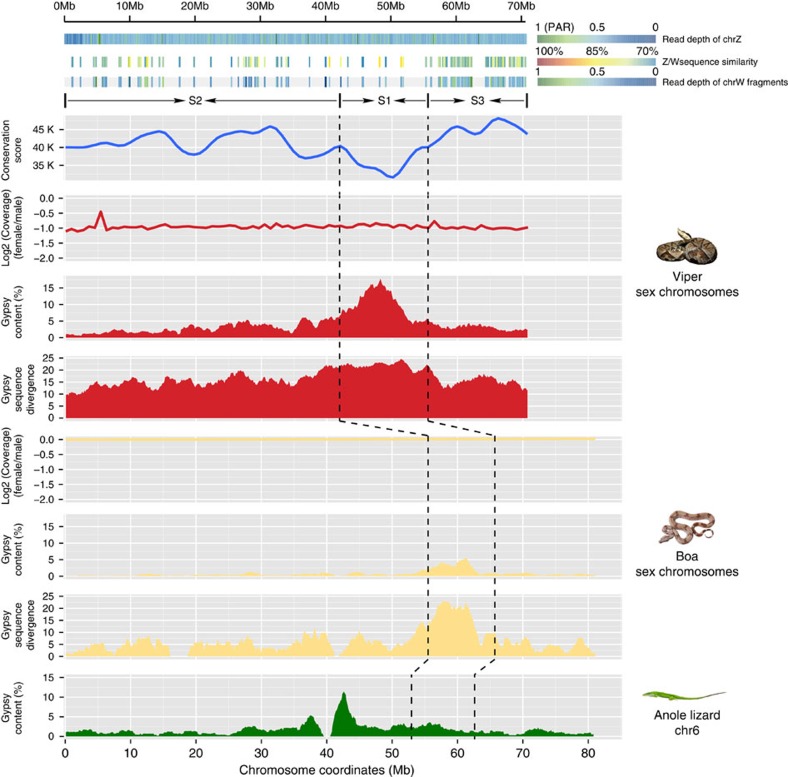
Figure 4. Snake sex chromosomes have at least three evolution strata.
The three tracks in the top panel shows female read depths along the Z chromosome relative to the median depth value of autosomes, Z/W pairwise sequence divergence within intergenic regions, and female read depths of W-linked sequence fragments relative to the median depth value of autosomes. Depths close to 1 suggest that the region is a recombining pseudoautosomal region (PAR), whereas depths of 0.5 are expected in a highly differentiated fully sex-linked region where females are hemizygous. The identifiable W-linked fragments are much denser at the region 56–70 Mb, probably because this region (denoted as stratum 3, S3) has suppressed recombination most recently. S2 and S1 were identified and demarcated by characterizing the sequence conservation level (measured by LASTZ alignment score, blue line) between the chrZs of boa and viper. At the oldest stratum S1 where recombination has been suppressed for the longest time, there is an enrichment of repetitive elements on the affected Z-linked region (Gypsy track in red, 100 kb non-overlapping sliding window). And these Z-linked TEs A similar pattern was found in homologous recombining region of boa, but not in lizard.