Figure 1.
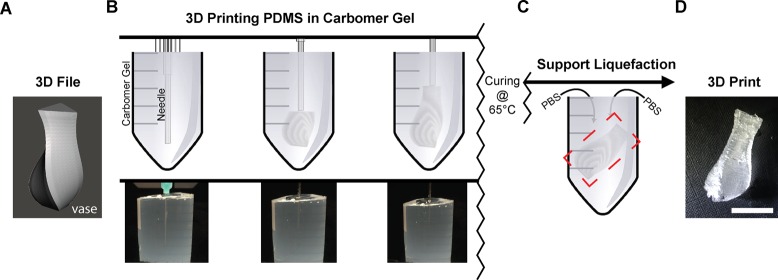
FRE printing is performed by extruding PDMS prepolymer in a support bath consisting of Carbopol gel. (A) A 3D file of a vase is imported and processed into G-code before being 3D printed. (B) The 3D file is replicated, layer-by-layer, from PDMS embedded within the Carbopol support bath by a syringe-based 3D printer. (top) A schematic of the printing process showing the vase in (A) printed within a 50 mL centrifuge tube filled with Carbopol. (bottom) A photograph of the actual vase being 3D printed from PDMS in the Carbopol, due to similar index of refraction it is difficult to see the vase. After printing the PDMS is cured for 72 h at room temperature or 2 h at 65 °C. (C) Following curing of the embedded PDMS, the Carbopol bath is liquefied by addition of monovalent cations, in this case a PBS solution, combined with mechanical agitation. (D) After the support bath is liquefied, the print can be removed. Scale bar is 1 cm.