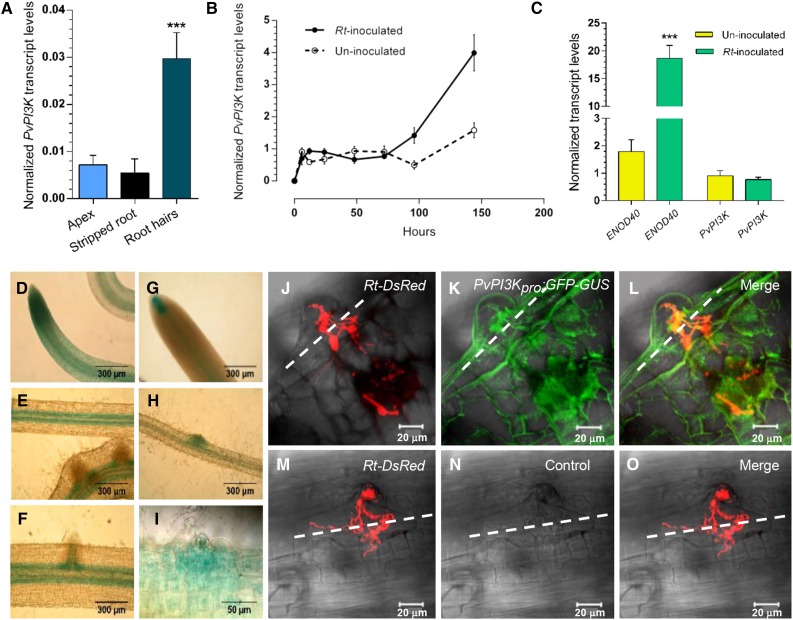
Figure 1.
Pv-PI3K Transcript Levels and Pv-PI3K Promoter Activity during the Early Stages of the Symbiosis between P. vulgaris and R. tropici CIAT 899.
(A) to (C) Quantification of transcript levels by RT-qPCR analysis.
(A) PI3K transcript levels were higher in root hairs than in the root apex and stripped roots collected from 2-d-old P. vulgaris seedlings. Bars represent the mean and sd (±sd) of two experiments (n = 2 from pool of 150 root tissues of seedlings treated to separate the apex and stripped roots).
(B) The level of Pv-PI3K transcript increases in wild-type P. vulgaris roots at 96 and 144 hai with R. tropici CIAT 899. At 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 hai, PvPI3K transcript levels in inoculated roots were comparable to those in uninoculated roots. Black line, roots inoculated with R. tropici CIAT 899; dotted line, uninoculated roots. Bars represent mean ± sd of three experiments (n = 3 from pool of 10 roots).
(C) An increase in Pv-ENOD40 transcript level in rhizobia-inoculated roots (72 hai) confirmed the activation of nodulation. No significant difference was found in Pv-PI3K transcript levels following inoculation. Bars represent mean (±sd) of three experiments (n = 3 from pool of 10 roots).
In (A) to (C), transcript levels were quantified by reverse transcription and real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) and calculated using levels of Elongation Factor 1α as reference, as described in Methods. Each RNA sample was assessed in triplicate. The number of biological replicates (n) is indicated. Error bars indicate mean and sd (±sd). For (A) and (B), statistically significant differences were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey´s test (***P < 0.0001). For (C), statistically significant differences were confirmed by an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test (***P < 0.001).
In (D) to (I), PvPI3Kpro:GFP-GUS activity in transgenic roots was detected at the root tip ([D] and [G]), the vascular tissue (E), and in the cells at the base of lateral root primordia (F), as assessed by GUS staining. When inoculated with R. tropici CIAT899, the Pv-PI3K promoter was highly active in the infected root hair (I) and in the cells adjacent to the infection site (H). Bars = 300 µm in (D) to (H) and 50 µm in (I).
(J) to (O) Hairy roots transformed with PvPI3Kpro:GFP-GUS were inoculated with R. tropici CIAT899 expressing the fluorescent marker DsRed (R. tropici-DsRed). Activity, detected as GFP fluorescence, was observed at the infection site (K) and merge in (L). Infection thread progression and ramification were traced by the fluorescence of DsRed (Rt-DsRed; red in [J] and [M]; merge in [L]). No green fluorescence was detected in P. vulgaris transgenic roots harboring a promoterless construct (control vector; [N]). White dashed lines indicate the border between the root epidermis and the adjacent cortical cell layer. Images were acquired in vivo using a Zeiss LSM 510 Meta Confocal Microscope; 21 optical sections each of 0.89 μm were acquired for PvPI3Kpro:GFP-GUS roots, and 16 optical sections each of 1.89 μm for the control roots. Transgenic roots were analyzed at 15 dai. Bars = 20 μm.