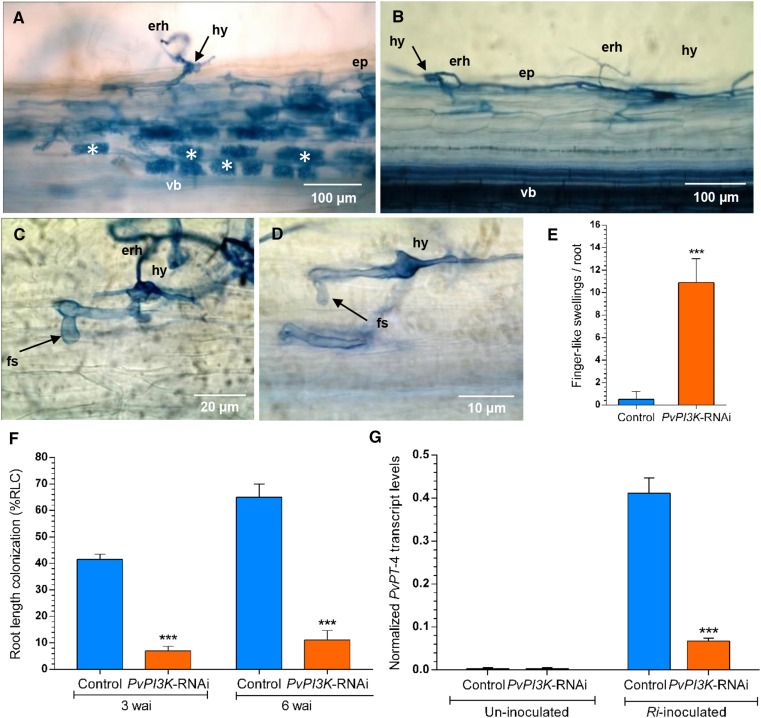
Figure 8.
Loss of Function of Pv-PI3K Impairs AM Symbiosis in P. vulgaris Roots.
(A) to (D) AM colonization in PvPI3K-RNAi and control TdT-Sac-RNAi transgenic roots (3 wai) was visualized using trypan blue staining. Bars = 100 μm in (A) and (B), 20 μm in (C), and 10 μm in (D).
(A) Control transgenic roots showing typical AM colonization with abundant arbuscules.
(B) PvPI3K-RNAi transgenic roots exhibited sparse hyphae entering and branching inside epidermal cells.
(C) and (D) Extraradical hyphae forming branched swellings known as hyphopodia were found. No arbuscules were observed. erh, extraradical hyphae; ep, epidermis; fs, finger-like swelling or outgrowth; hy, hyphopodium; vb, vascular bundle; asterisks, arbuscules.
(E) The number of finger-like outgrowths was higher in PvPI3K-RNAi transgenic roots than in control (TdT-Sac-RNAi) roots inoculated with R. irregularis and collected at 3 wai. Data are means ± sd from three independent experiments (n = 33). Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test (***P < 0.001).
(F) AM colonization was impaired by the loss of function of Pv-PI3K. The root length colonization (%RLC) in PvPI3K-RNAi transgenic roots was lower than in control (TdT-Sac-RNAi) transgenic roots. The data represent means ± sd of three independent experiments (n = 39 roots). Statistical significance was determined using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test (***P < 0.001).
(G) Transcript level of PvPT-4, the molecular tracker of AM colonization. The expression of PvPT-4 was lower in PvPI3K-RNAi roots inoculated with R. irregularis than in inoculated control (TdT-Sac-RNAi) transgenic roots, as determined by RT-qPCR. Transcript levels were normalized to EF1α as reference gene. Calculations were made as described in Methods. The bars represent mean ± sd of two experiments (n = 2 from a pool of 12 transgenic roots). Asterisks represent statistically significant differences (unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test, **P < 0.004).