Figure 1.
The Genetic Model and Three-Line Hybrid Breeding Procedure of Genic Male Sterile System 7365ABC in B. napus.
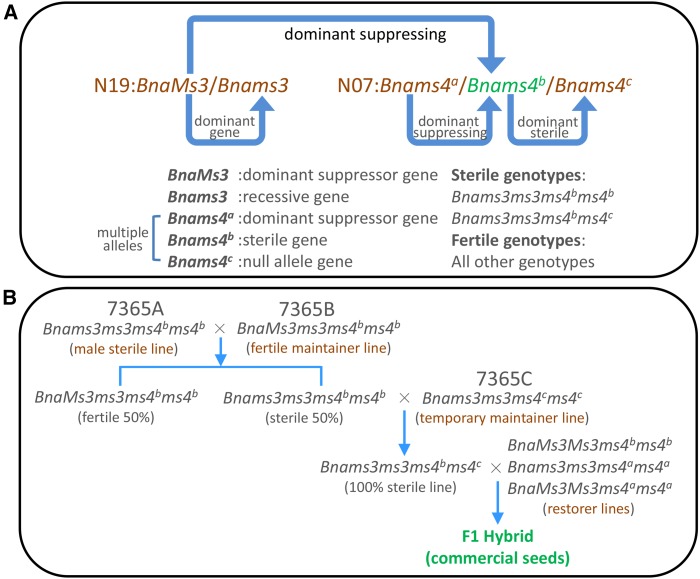
(A) The fertility of 7365ABC is controlled by two alleles of loci located in two different linkage groups: N07 and N19. The multigene locus (N07) consists of Bnams4a, Bnams4b, and Bnams4c. Bnams4b is a dominant male-sterile gene relative to the null allele Bnams4c; Bnams4b has two dominant suppressor genes BnaC9.Tic40 and Bnams4a. The locus N19 consists of BnaC9.Tic40 (BnaMs3) and BnaC9.tic40 (Bnams3). Curved blue arrows show the explicit-implicit relationships between these genes: BnaC9.Tic40>BnaC9.tic40 and Bnams4a>Bnams4b>Bnams4c. Therefore, only Bnams3ms3ms4bms4b and Bnams3ms3ms4bms4c are sterile for they have no suppressor gene, while Bnams3ms3ms4ams4b and BnaMs3ms3ms4bms4b are fertile as they each contain a suppressor gene. Bnams3ms3ms4cms4c is also fertile as it has no sterile gene Bnams4b, and this genotype can be used as temporary maintainer line.
(B) The genic male sterile breeding system 7365ABC consisted of male-sterile line 7365A (Bnams3ms3ms4bms4b), maintainer lines 7365B (BnaMs3ms3ms4bms4b) and 7365C (Bnams3ms3ms4cms4c), and restorer lines (BnaMs3Ms3ms4bms4b or Bnams3ms3ms4ams4a, etc.). First, male-sterile line 7365A is crossed with maintainer line 7365B to generate a 1:1 ratio of fertile and sterile plants; second, the sterile plants are crossed with temporary maintainer line 7365C to generate a 100% completely sterile population; this population makes manual removal of 50% fertile plants in field during hybrid seed production of large area unnecessary, compared with using other types of genic male sterile systems. Subsequently, the 100% sterile population was extensively tested with a variety of restorer lines to produce superior hybrid seed. This kind of genic male sterile system has extensive restorer lines, compared with cytoplasmic male sterile lines, due to the wide distribution of suppressor genes (BnaC9.Tic40 and Bnams4a) in natural varieties or inbred lines.