Figure 7.
Bnams4a Probably Rescued the Sterility by Suppressing Expression of the Chimeric ORF.
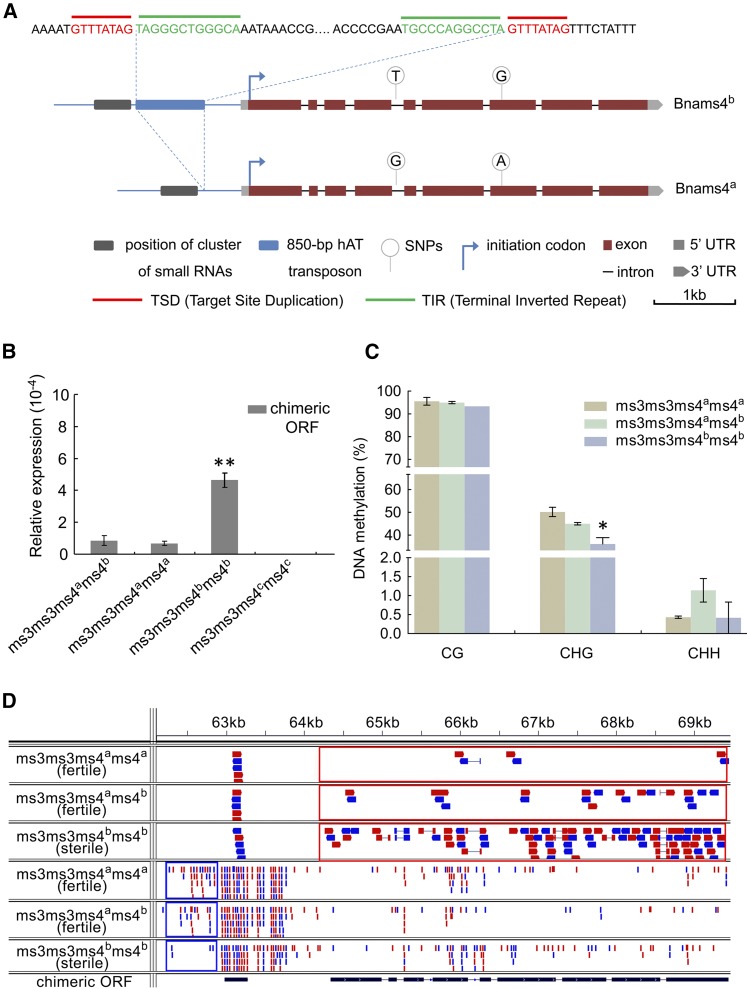
(A) Structure comparison of the chimeric genes in Bnams3ms3ms4ams4a (Bnams4ams4a-chimeric-ORF) and Bnams3ms3ms4bms4b (Bnams4b) from NIL 736512AB. It shows an insertion of 850-bp MITE in the Bnams4b regulatory region but not in regulatory region of the Bnams4ams4a-chimeric-ORF. Although there are two SNPs between Bnams4ams4a-chimeric-ORF and Bnams4b, both of them can lead to male sterility in A. thaliana. This suggests both the chimeric ORF in Bnams3ms3ms4ams4a and Bnams3ms3ms4bms4b are functional in causing sterility.
(B) The transcript level of the chimeric ORF in three kinds of genotypes from self-crossing of fertile individuals in NIL 736512AB. By self-crossing, the fertile individuals in NIL 736512AB produced three genotypes: Bnams3ms3ms4ams4a (fertile), Bnams3ms3ms4ams4b (fertile), and Bnams3ms3ms4bms4b (sterile). The anthers from about the tetrad stage (buds of 1.5 to 2 mm) were used for analysis. 7365C (Bnams3ms3ms4cms4c) which did not contain Bnams4b was used as negative control.
(C) DNA methylation analysis of the small RNA regions of Bnams4ams4a-chimeric-ORF and Bnams4b by bisulphite-based method. It shows methylation level of CHG type is higher in the small RNAs region of Bnams4ams4a-chimeric-ORF than the sterile genotype: Bnams3ms3ms4bms4b. All data represent mean ± sd. *P < 0.05.
(D) Integrative Genomics Viewer screen capture of RNA-seq reads mapping to chimeric ORF. The three panels above showed transcriptome sequencing reads (∼100 bp), while three panels below represented microRNA sequencing reads (∼21 to 24 bp). These results suggested that a cluster of microRNA (blue box) in promoter region might repress the expression of chimeric ORF (red box). Both sense (represented in red) and antisense (represented in blue) strand reads are shown.