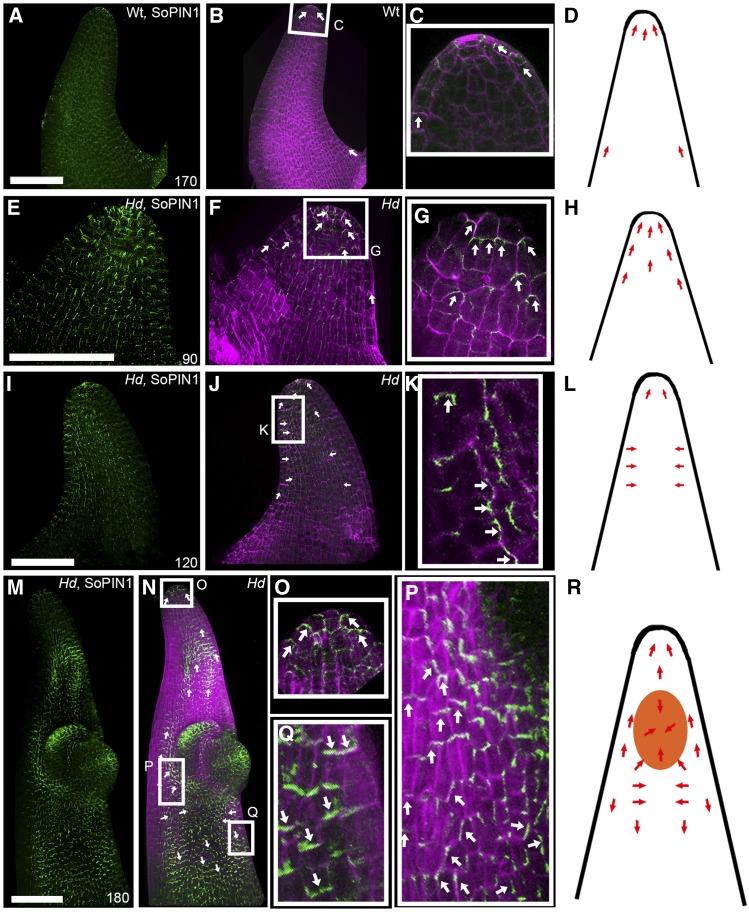
Figure 5.
SoPIN1 Localization Reorients When Ectopic BKn3 Expression Is Activated.
3D projections of whole-mount immunolocalization of SoPIN1 (green) and calcofluor-stained cell walls (magenta) in whole wild-type lemmas at 170 h ([A] to [D]) and Hd lemmas at 90 h ([E] to [H]), 120 h ([I] to [L]), and 180 h ([M] to [R]). Orientation of SoPIN1 is based on cellular SoPIN1 localization in the epidermal layer only. Each panel illustrates SoPIN1 localization alone ([A], [E], [I], and [M]), both SoPIN1 and calcofluor combined ([B], [F], [J], and [N]), and a zoomed-in image of the boxed regions ([C], [G], [K], [O], [P], and [Q]), alongside a cartoon illustrating the inferred relationship between the ectopic meristem (orange) and SoPIN1 localization (red arrows) ([D], [H], [L], and [R]). Overlapping SoPIN1 and calcofluor signals appear white. In wild-type lemmas, SoPIN1 pointed distally toward the lemma tip throughout development ([A] to [D]), although SoPIN1 signal in the adaxial surface was lost over developmental time. In Hd lemmas, SoPIN1 signal was not lost over developmental time ([E] to [R]). Before BKn3 was ectopically expressed in the Hd lemma, SoPIN1 was localized distally, toward the tip of the developing lemma ([E] to [G], white arrows; [H], red arrows). Around the time that ectopic BKn3 expression was activated in the lemma (110 h), SoPIN1 localization reoriented (with respect to earlier stages in development) in the adaxial surface. Initially, SoPIN1 oriented laterally toward the center of the adaxial surface ([I] to [K], white arrows; [L], red arrows). After the ectopic meristem had formed ([M] to [R], 180 h), near the distal tip, cellular SoPIN1 was oriented distally toward the tip of the lemma (O), below the ectopic meristem SoPIN1 pointed toward the center of the adaxial surface (P), and below this SoPIN1 was oriented proximally ([Q], white arrows; [R], red arrows). n = 4 for each time point. Bars = 100 μm.