Figure 3.
Functional Link between DDB2 DNA Binding Capacity and DNA Methylation.
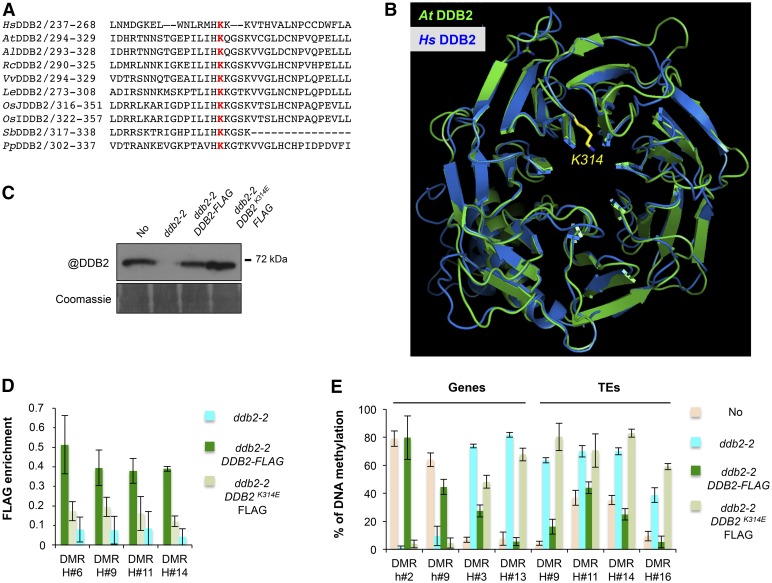
(A) Amino acid alignment of the human DDB2 protein domain surrounding K244 with various plant homologs. Hs, Homo sapiens; At, Arabidopsis thaliana; Al, Arabidopsis lyrata; Rc, Ricinus communis; Vv, Vitis vinifera; Le, Lycopersicon esculentum; OsJ, Oryza sativa group Japonica; OsI, Oryza sativa group Indica; Sb, Sorghum bicolor; Pp, Populus populi. K314, involved in DNA binding and highlighted in red, is highly conserved among all analyzed sequences.
(B) In silico prediction of the structural conservation of Arabidopsis DDB2 protein (green) upon modeling with the human (blue) DDB2 protein structures. K314 is shown in yellow.
(C) Immunodetection of the DDB2-FLAG proteins in ddb2-2/DDB2-FLAG and in ddb2-2/DDB2K314E-FLAG-expressing plants using an anti-DDB2 antibody. Wild-type (No) and ddb2-2 plants were used control. Coomassie blue staining of the blot is shown.
(D) ChIP-qPCR analysis of DDB2 enrichment at hyper-DMR over four TEs in ddb2-2/DDB2-FLAG and ddb2-2/DDB2K314E-FLAG-expressing plants using an anti-FLAG antibody. ChIP performed with ddb2-2 plants with anti-FLAG antibody was used as the negative control. Data are presented as enrichment of FLAG signal (±sd) and are representative of three biological replicates.
(E) Complementation assay for DMRs overlapping two genes and four TEs in ddb2-2/DDB2-FLAG and ddb2-2/DDB2K314E-FLAG expressing plants. Wild-type (No) and ddb2-2 mutant plants were used as controls. Data are presented as percentage of methylation (±sd) and are representative of three biological replicates measured by McrBC-qPCR. H, hyper-DMR; h, hypo-DMR.