Figure 5.
Characterization of the DDB2-AGO4 Protein Complex.
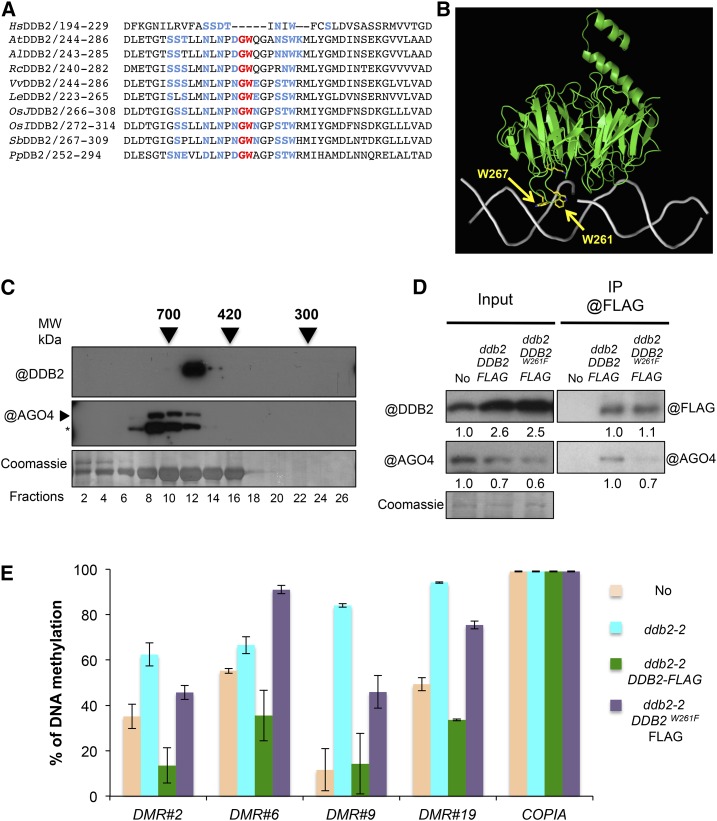
(A) Amino acid alignment of the Arabidopsis DDB2 protein domain surrounding the GW motif with various plant and human homologs. The GW motif (red) absent in human but conserved among plant DDB2 proteins. Surrounding key amino acids that define the AGO hook are shown in blue. Species abbreviations are given as in Figure 3.
(B) In silico modeling of the Arabidopsis DDB2 protein structure (green) bound to a DNA helix (gray). Tryptophan residues (W) surrounding the GW motif and K314 are exposed to the DNA helix (gray) and shown in yellow.
(C) Size-exclusion chromatography analysis of the DDB2 complex in soluble protein extracts from wild-type (Col) plants. The indicated fractions were analyzed by immunoblot using anti-DDB2 and anti-AGO4 antibodies. Arrows indicate elution peaks of molecular weight standards in the same conditions. Coomassie blue staining of the blot is shown. Asterisk indicates cross-reacting signal.
(D) In vivo pull-down of AGO4 with DDB2 protein. Wild-type (No), ddb2-2/DDB2-FLAG, and ddb2-2/DDB2W261F-FLAG expressing plants were used for immunoprecipitation assays using anti-FLAG antibody. Coomassie blue staining of the blot is shown. Signal intensity relative to control is given below each lane.
(E) Complementation assay for four DMR overlapping TEs in ddb2-2/DDB2-FLAG and ddb2-2/DDB2W261F-FLAG expressing plants. Wild-type (No) and ddb2-2 mutant plants were used as controls. Data are presented as percentage of methylation (±sd) and are representative of three biological replicates measured by McrBC-qPCR. The COPIA TE was used as control.