Figure 12.
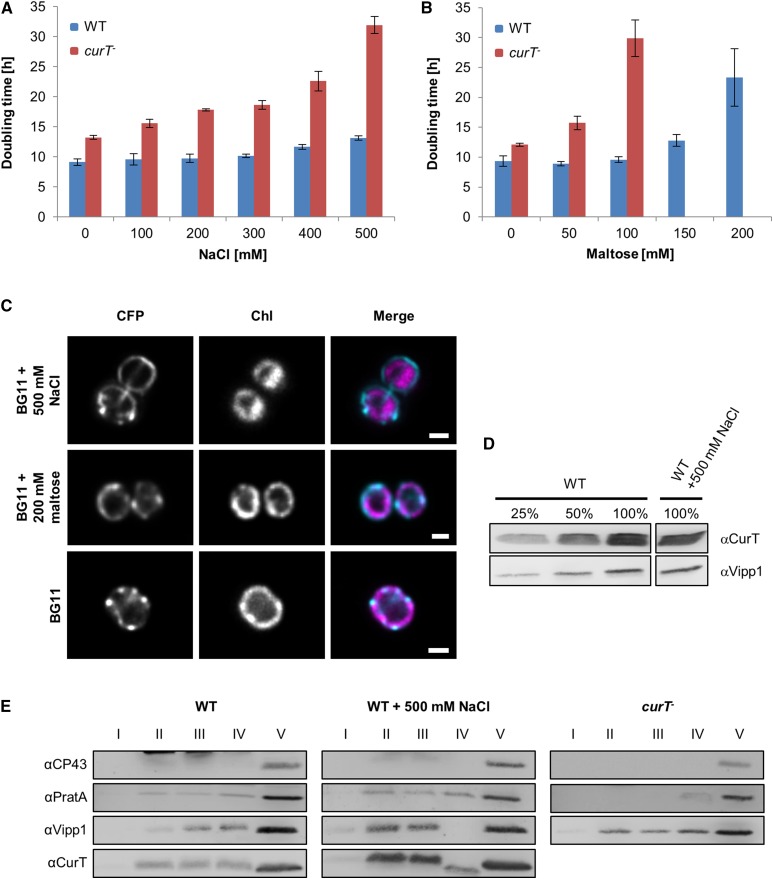
Loss of CurT Increases Sensitivity to Abiotic Stress.
(A) and (B) Doubling times of wild-type and curT- under salt stress (A) or osmotic stress (B). Doubling times are means ± sd of three independent cultures.
(C) Localization of CurT-CFP under salt and osmotic stress. Samples were examined as described in Figure 8. Bars = 1 µm.
(D) Protein levels of wild-type cells after growth in BG11 medium containing 500 mM NaCl. Samples were analyzed on the same gel, but unrelated samples between the presented signals were omitted.
(E) Membrane preparations obtained from wild-type cells, wild-type cells grown in the presence of 500 mM NaCl, and curT- cells were subjected to the first gradient step in the membrane fractionation scheme. The gradient was divided into five fractions, and 10% of fractions I to IV and 0.2% of fraction V were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Fraction II includes the plasma membrane and fraction V consists of PratA-defined membrane and thylakoid membrane.