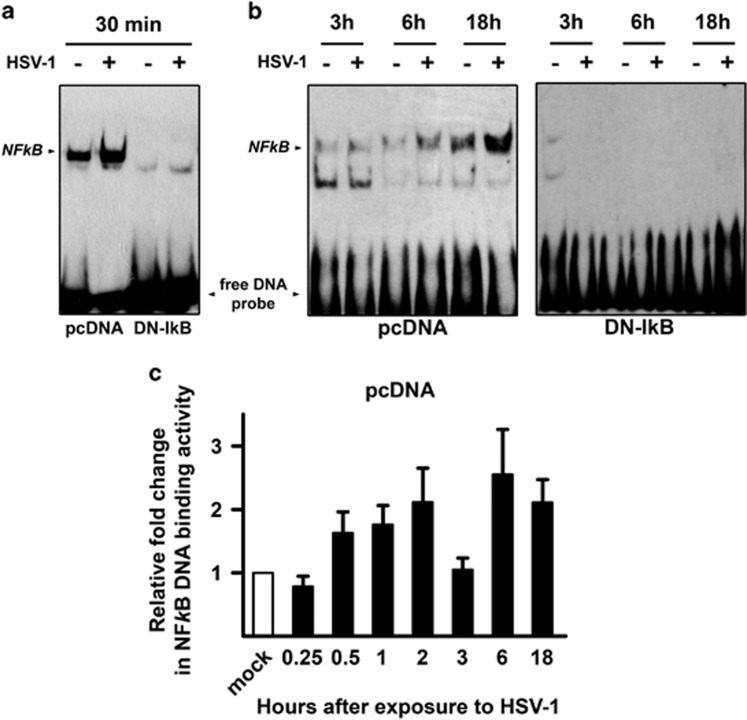
Figure 1.
NF-κB DNA binding activity by EMSA in U937 monocytic cells infected by HSV-1. U937 cells stably transfected with an empty control vector (pcDNA) or with a dominant negative (DN) mutant of murine IκBα (DN-IkB), were mock infected (−) or infected (+) with 50 MOIs of HSV-1. At 30 min or 3, 6 and 18 h after the first exposure to virus, nuclear extracts were prepared and NF-κB activation was measured by EMSA. pcDNA and DN-IkB samples collected at 30 min were run in the same gel (a), while pcDNA and DN-IkB samples collected at the other time points were run in separate gels (b). The position of the NF-κB DNA is indicated. EMSA gels from one representative experiment of the three performed are shown. (c) Quantitative analysis of the data shown in (a) and (b) using densitometry image analysis of the EMSA gels. Results are expressed as fold change in band intensities from HSV-1- versus mock-infected samples at the same time point. Data represent the mean values±s.d. of three separate experiments for each time course. Multiple comparisons by Bonferroni's post-hoc ANOVA test gave the following results for time 0.25 h versus other times: versus 1 h, P=0.044; versus 2 h and versus 18 h, P=0.002; versus 6 h, P<0.001; versus all other times, not significant. No appreciable optical densitometry value was detected in EMSA gels from parallel time course experiments in U937-DN-IκB cells (data not shown)