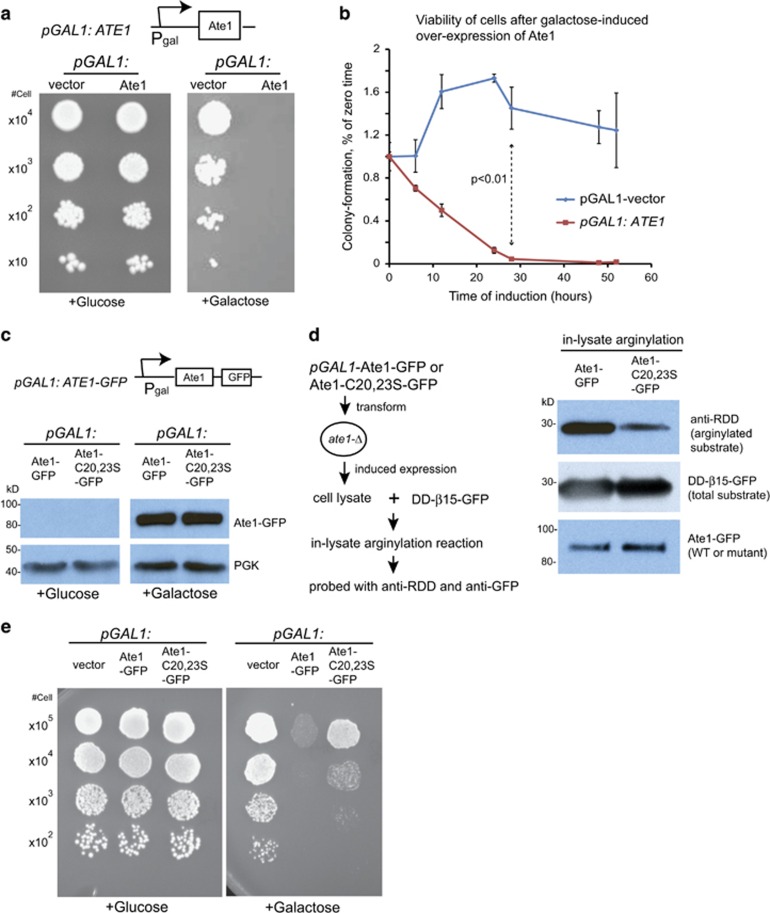
Figure 5.
The increase of Ate1 triggers cell death in yeast in a manner that is dependent on its arginylation activity. (a) The scheme in the top panel shows the domain structure of plasmid pGAL1: ATE1, in which the coding sequence of recombinant protein is preceded by the inducible GAL1 promoter. The picture in the bottom panel shows the growth of ate1Δ yeast cells carrying either the empty expression vector or pGAL1: ATE1 by a serial dilution growth assay on either plate containing glucose (suppressing) or galactose (inducing). (b) Graph showing the viabilities of ate1Δ yeast cells carrying either the empty expression vector or pGAL1: ATE1 in different time points following the initiation of galactose-induced expression, as measured by the numbers of colony-forming cells per OD unit (CFU) that were normalized to starting data point time 0, for Ate1 or vector control separately. Error bar represents S.E.M. (n⩾3). (c) The top scheme shows the domain structure of a recombinant Ate1 fused with a linker and a C-terminal GFP, driven by the pGAL1 promoter, termed ‘pGAL: Ate1-GFP'. Immunoblot analysis of the steady-state levels of wild-type and C20,23S mutant Ate1 after 9-h culture in the presence of non-inducing (glucose) or inducing (galactose) carbon sources. PGK was used as loading controls. Anti-GFP was used to probe the steady-state levels of the recombinant ‘pGAL: Ate1-GFP' (WT or mutant). (d) Left panel showing the procedure of using an in-lysate arginylation assay to measure the activities of recombinant Ate1-GFP, either the WT version or the C20,23S mutant, which were expressed for 9 h in ate1Δ yeast (see c for the steady-state levels of expressed proteins). Anti-RDD was used to indicate the level of arginylated reporter. Anti-GFP was used to show the total amount of reporter protein (DD-β15-GFP) in each sample, as well as the total amount of Ate1-GFP (either WT or mutant) present in each sample. These two bands were distinguished by their difference in molecular weight (27 kDa versus 92 kDa). (e) Representative pictures of growth test using serial dilutions of ate1Δ yeast carrying either the empty expression vector or pGAL1-Ate1-GFP, or pGAL1-Ate1-C20,23S-GFP, in media containing non-inducing (glucose) or inducing (galactose) carbon sources