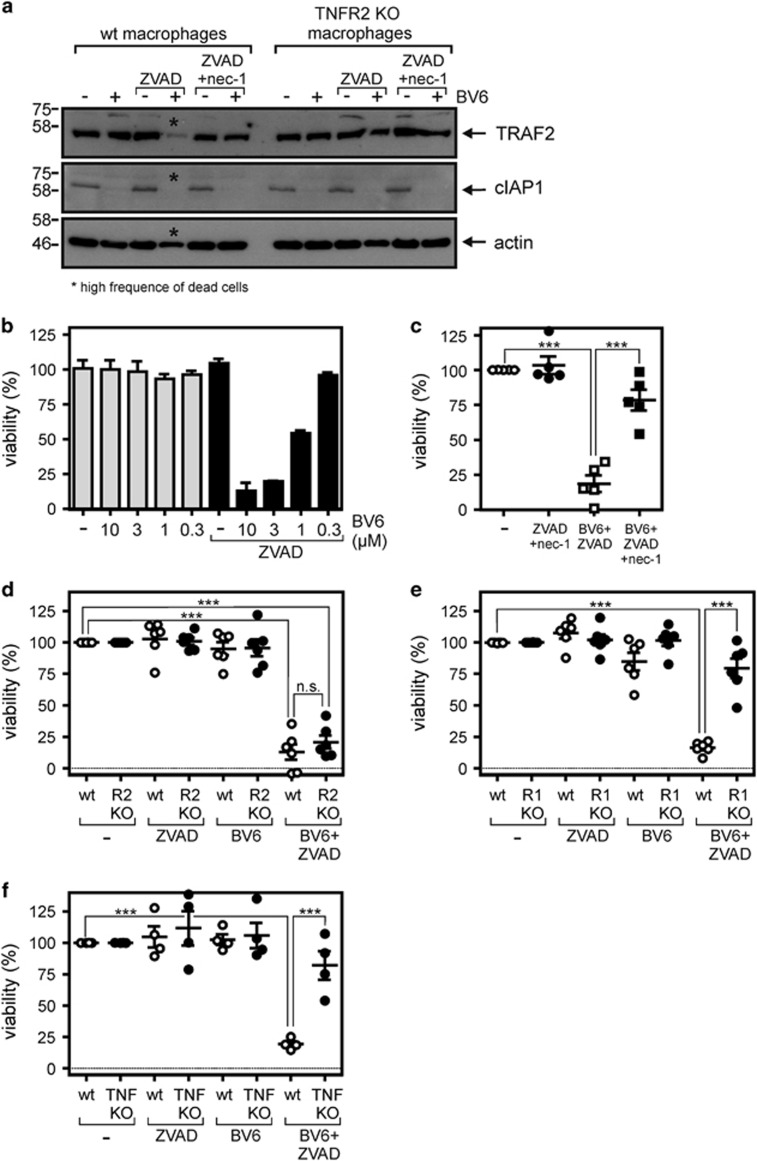
Figure 4.
BV6 induces necroptosis in murine macrophages. (a) Wild type and TNFR2-deficient macrophages derived from HoxB8-immortalized MPCs were challenged for 7 h with the indicated combinations of BV6 (10 μM), zVAD-fmk (20 μM) and necrostatin-1 (45 μM). Cells were finally analyzed by western blotting for the presence of TRAF2 and cIAP1. Please note, wild-type cells treated with BV6 and zVAD-fmk were already largely dead when cells were harvested for Western blot analysis. (b) Macrophages derived from HoxB8-immortalized MPCs were stimulated in triplicates (technical replicates) with the indicated concentrations of BV6 in the presence and absence of 20 μM zVAD-fmk and analyzed for viability after 36 h. One of four representative experiments is shown. (c) HoxB8-immortalized MPC-derived macrophages were challenged with the indicated mixtures of 10 μM BV6, 20 μM ZVAD-fmk and 45 μM necrostatin-1 and analyzed for viability after 36 h. Shown are data points with S.E.M. of five independent experiments. (d–f) Macrophages derived from Hoxb8 immortalized MPCs of wild type, TNF- (d), TNFR1- (e) and TNFR2-deficient mice (f) were stimulated with the indicated combinations of BV6 (10 μM) and zVAD-fmk (20 μM). After 36 hours cell viability was quantified using MTT assay or crystal violet staining. Data points derived from six (d and e) or four (f) independent experiments together with mean±S.E.M. are depicted. ***p<0.001