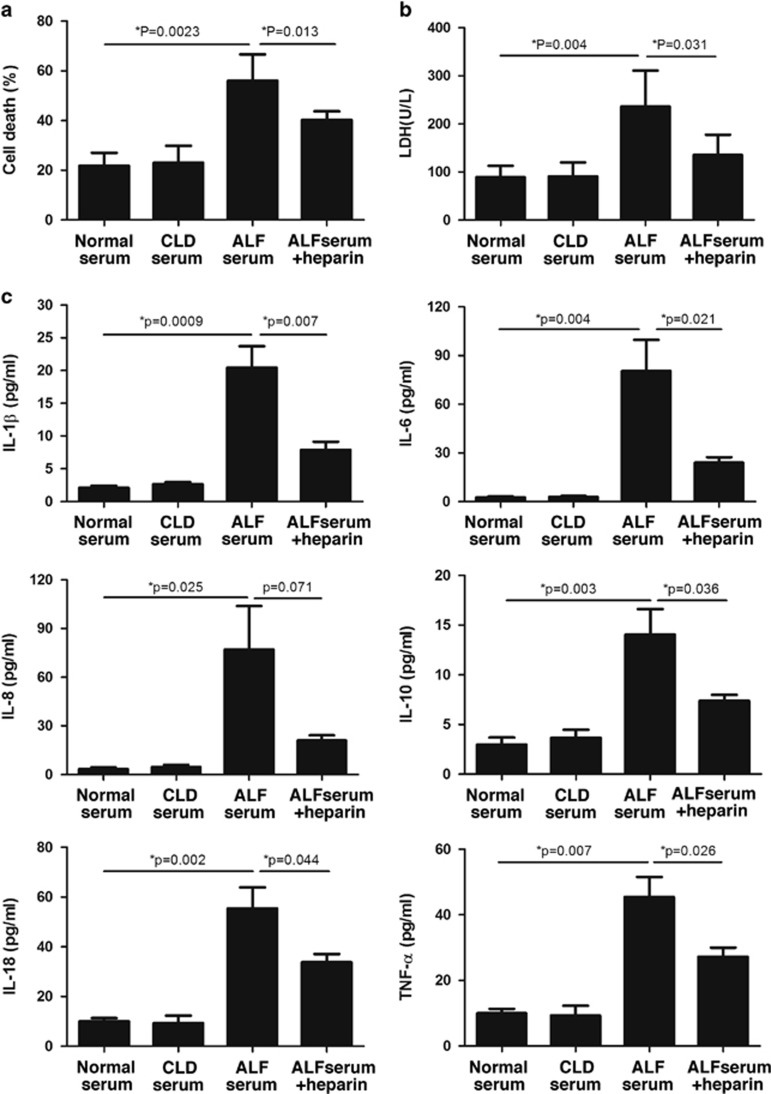
Figure 3.
ALF patients' sera induced human L02 hepatocyte death and stimulated human monocyte U937 to produce cytokines. (a) It showed that ALF patients' sera could drastically decrease cell viability of human L02 hepatocytes after 24-h incubation as compared with CLD patients or healthy controls' sera, whereas addition of noncoagulant heparin could inhibit cell death caused by ALF patients' sera. (b) Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels were significantly increased in supernatant of human L02 cells after stimulation of ALF patients' sera in contrast to the sera from CLD patients or healthy controls, whereas addition of noncoagulant heparin could reduce LDH levels. (c) The six cytokines were all notably increased in the supernatant of ALF serum-treated human monocytic U937 cells, whereas addition of noncoagulant heparin could decrease the levels of these cytokines. (*P<0.05) Variables were expressed as mean±S.D. The experiments were repeated at least three times