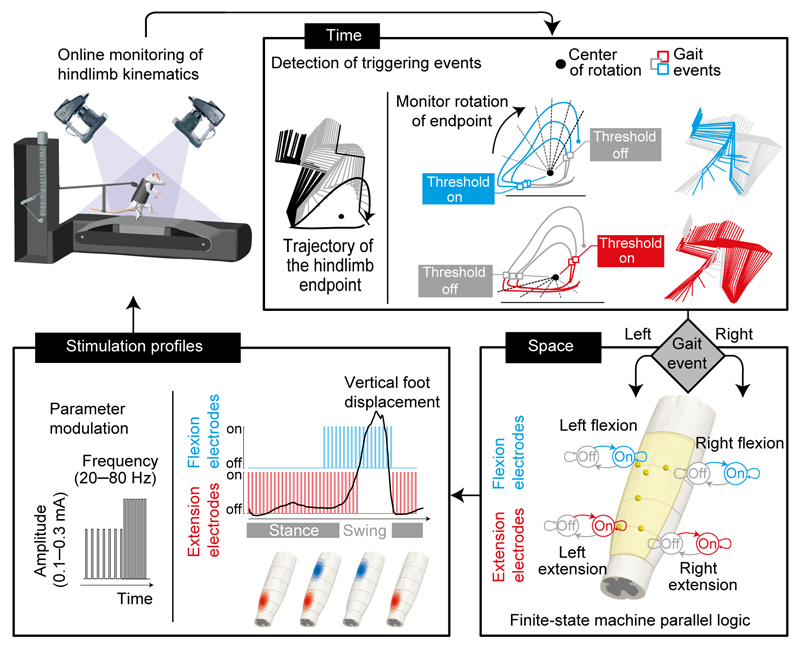
Figure 3. Software to adjust spatiotemporal neuromodulation in real–time during locomotion.
Computational platform to trigger adjustments of the temporal structure, spatial configuration and stimulation parameters of the neuromodulation therapies. Rats were supported bipedally in a robotic system provided vertical support during locomotion onto a motorized treadmill belt. A high–resolution video system allowed real–time monitoring of the left and right hindlimb endpoints (feet). The angular displacements of hindlimb endpoints around a calculated center of rotation were converted into angular coordinates, as indicated with the dotted grey lines. The on and off states of electrodes targeting extensor– and flexor–related hotspots were triggered when the angular coordinates crossed user–defined thresholds, personalized for each rat. The stimulation profile module enabled tuning the amplitude and frequency of stimulation based on the therapist or control policies. The diagram represents the relationship between the vertical displacement of the foot and the activation of extensor and flexor hotspot, and how the spatially selective electrodes were turned on and off to replicate this activation pattern.