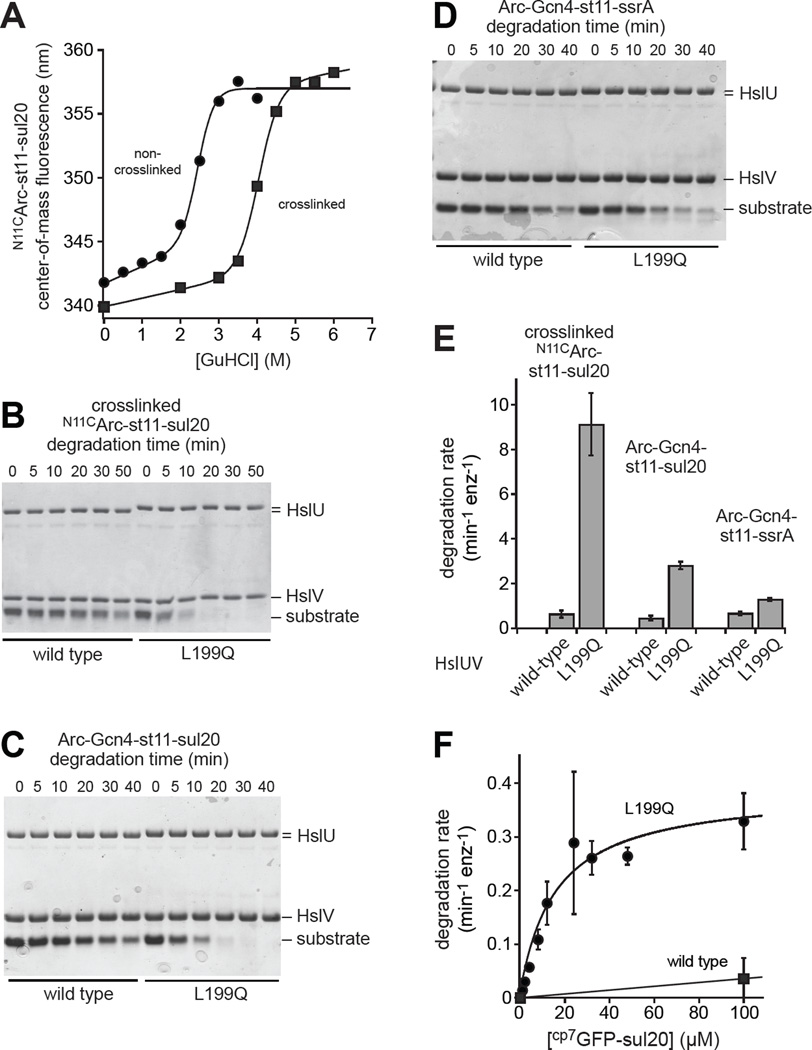
Figure 5. Degradation of substrates differing in structure and stability.
(A) Stability to GuHCl denaturation of N11CArc-st11-sul20, before and after crosslinking with 1,6-bismaleimidoethane, monitored by changes in tryptophan fluorescence. (B) Degradation monitored by SDS-PAGE of crosslinked N11CArc-st11-sul20 (20 µM) by WTHslUV or L199QHslUV (300 nM HslU; 500 nM HslV). (C) Degradation monitored by SDS-PAGE of Arc-Gcn4-st11-sul20 (15 µM) by WTHslUV or L199QHslUV (500 nM HslU; 1000 nM HslV). (D) Degradation monitored by SDS-PAGE of Arc-Gcn4-st11-ssrA (15 µM) by WTHslUV or L199QHslUV (500 nM HslU; 1000 nM HslV). (E) Rates of degradation of crosslinked N11CArc-st11-sul20, Arc-Gcn4-st11-sul20, and Arc-Gcn4-st11-ssrA by WTHslUV and L199QHslUV. Rates were determined by single-exponential fits of substrate remaining versus time determined by densitometry of the gels in panels B-E plus two additional independent replicates for each substrate. The values plotted are averages of the three replicates ± SD. (F) Michaelis-Menten plot for degradation of cp7GFP-sul20 by WTHslUV or L199QHslUV (500 nM HslU; 1000 nM HslV). Values are averages (n=3) ± SD. Fitted parameters for L199QHslUV are listed in Table 2. For WTHslUV, the line is a linear function and KM and Vmax were not determined. All degradation assays were performed at 37 °C in the presence of 5 mM ATP.