Figure 6.
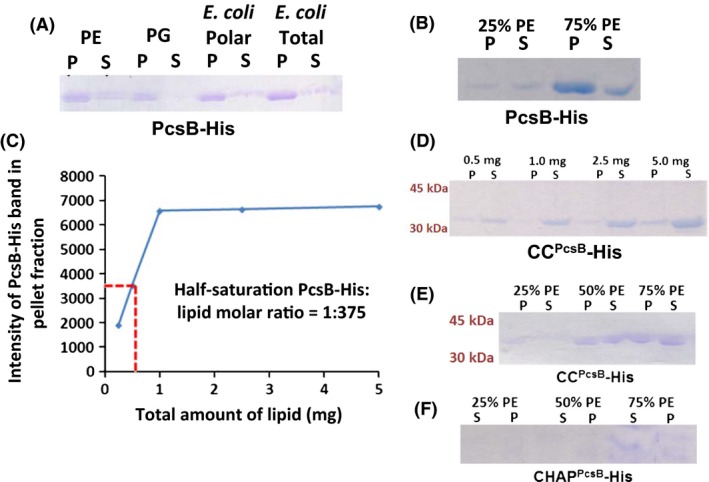
Liposome sedimentation binding assays of purified PcsB‐His and its CCP csB‐His and CHAPP csB‐His domains. Liposomes containing the indicated phospholipids (5 mg total lipids unless noted otherwise) were prepared, bound to PcsB‐His, CCP csB‐His, or CHAPP csB‐His, and collected by centrifugation as described in Materials and Methods. Amounts of protein bound to washed liposome pellets (P) or remaining in supernates (S) were determined by densitometry of SDS‐PAGE gels. (A) PcsB‐His binding to liposomes containing 50% phosphatidylcholine (neutral head group) + 50% phosphatidylethanolamine (positively charged head group) (PE); 50% phosphatidylcholine + 50% phosphatidylglycerol (negatively charged head group) (PG); E. coli polar lipids; or E. coli total lipids. (B) PcsB‐His binding to liposomes containing increasing proportions of PE (25% to 75%) compared to phosphatidylcholine (PC); (C) Binding assay of PcsB‐His to liposomes containing different total amounts of a mixture of 50% PE + 50% PC to determine the half‐saturation ratio of binding. Data points were averaged from two different experiments. (D) Binding of CCP csB‐His domain to liposomes containing different total amounts of a mixture of 50% PE + 50% PC. (E) CCP csB‐His binding to liposomes containing increasing proportions of PE (25–75%) compared to phosphatidylcholine (PC). (F) Minimal binding of CHAPP csB‐His to liposomes containing increasing proportions of PE (25–75%) compared to phosphatidylcholine (PC). All experiments were performed at least two times independently with similar results.
