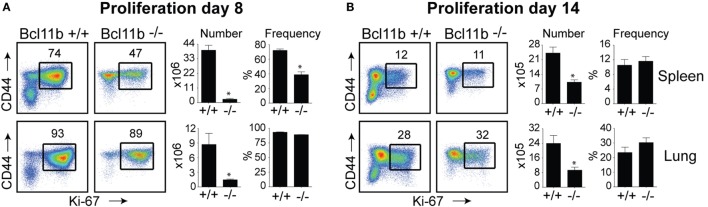
Figure 2.
Bcl11b controls the magnitude of expansion of virus-specific CD8 T cells in response to VacV-WR infection. WT (Bcl11bflox/flox/dLck-iCre−; n = 8) or Bcl11b-conditional knockout (Bcl11bflox/flox/dLck-iCre+; n = 7) mice were infected i.p with VacV-WR (2 × 105 PFU/mouse). Eight (A) and 14 (B) days postinfection, splenocytes and lung cells were harvested and stained for CD8, CD44, and Ki67. (A,B) Left, Representative plots showing the percentage of CD8 T cell proliferation by Ki67 staining among CD44hi cells in VacV-infected mice. Right, total numbers and percentages of CD8+CD44hiKi67+ cells per spleen and lung. Quadrant settings were based on controls, after gating on naïve CD44lo cells in the same host. Percentages that stained positive for each marker are indicated. The results shown are representative of two separate experiments each with three to four mice per group. Asterisks indicate statistical significance. The p-values are <0.05 by two-tailed Student t-test (WT vs. Cko).