FIGURE 1.
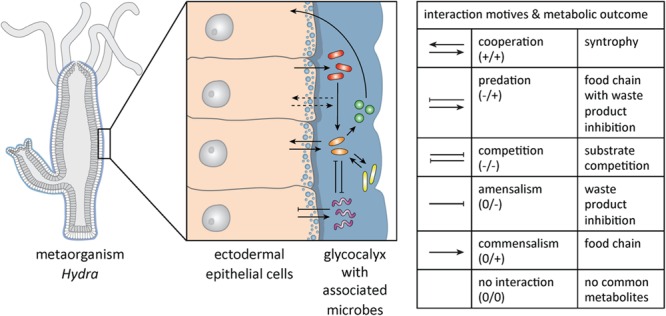
Complex microbial community interactions in Hydra. Schematic drawing of Hydra, with a magnified section of the ectodermal epithelial cells that are covered with a glycocalyx and the associated microbial community. In this complex system microbes may interact with each other in multiple ways as depicted by arrows. For the species involved interactions can have a positive (+), a negative (-) or no impact (0). A summary of the possible ecological interactions and their meaning in metabolic terms are summarized in the table (modified from West et al., 2007; Faust and Raes, 2012; Großkopf and Soyer, 2014). It is likely that interactions between specific microbes and the host can be modulated by metabolic or physical signals but that the host also directly affects the interaction between microbial species (dashed arrows) via epithelial selection.
