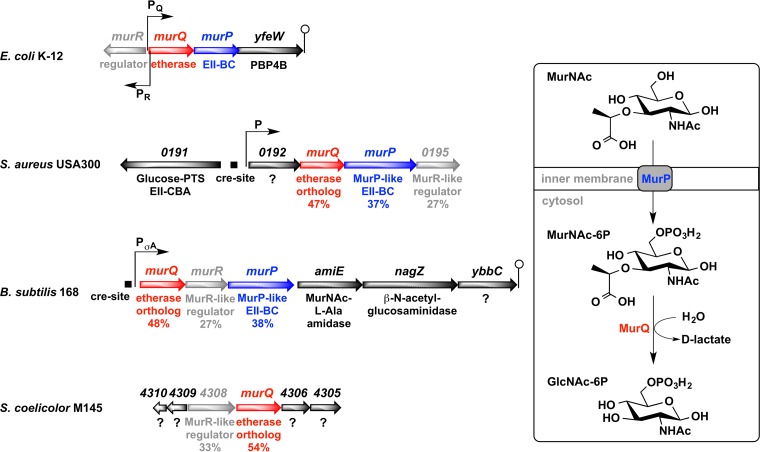
FIG 1 .
MurQ operon (MurNAc-recycling divergon) and MurNAc catabolic pathway in E. coli (top and right, respectively), and organization of chromosomal regions of murQ orthologs of the Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus, B. subtilis, and S. coelicolor. The schematic of the organization of the E. coli K-12 murQ operon genes includes the promoters for transcription of the murQ operon (Pq) and murR (PR) and the terminator (lollipop), according to Jaeger and Mayer (20). murQ encodes MurNAc-6P etherase, murP encodes the MurNAc-specific phosphotransferase system (PTS) transporter EII-BC domain, and yfeW encodes the low-affinity penicillin binding protein 4B (PBP4B). Upstream from the murQ gene and divergently transcribed is the murR gene, a transcriptional repressor of the MurNAc recycling divergon. The schematic for S. aureus USA300 (NCBI Reference Sequence accession no. NC_007793.1) shows putative genes for MurNAc utilization, as well as the proteins they encode. SAUSA300_0192 encodes a protein whose function is unknown, SAUSA_0193 encodes an ortholog of MurQ, SAUSA_0194 encodes an MurP-like PTS EII-BC domain protein, and SAUSA_0195 encodes a MurR-like regulator. The schematic for B. subtilis 168 (NCBI Reference Sequence accession no. NC_000964.3) shows the putative promoter PσA in front of the recycling cluster of 6 genes, including murQ (formerly ybbI), murR (formerly ybbH), murP (formerly ybbF), encoding the MurP EII-BC domain, amiE (formerly ybbE), encoding the MurNAc-l-alanine amidase AmiE, nagZ (formerly ybbD), encoding the N-acetylglucosaminidase NagZ, and ybbC, encoding a protein whose function is unknown. The schematic for S. coelicolor A3(2)/M145 (NCBI Reference Sequence accession no. NC_003888.3) shows a putative cluster of genes for MurNAc recycling that includes SCO4308, encoding a MurR-like regulator, and SCO4307, encoding an ortholog of MurQ, as well as two open reading frames encoding proteins whose functions are unknown, SCO4305 and SCO4306. The amino acid sequence identities (%) of orthologous proteins relative to the sequences of E. coli MurQ, MurP, and MurR are shown. Catabolite-responsive elements (cre sites) were identified in the promoter regions upstream from the murQ genes of B. subtilis and S. aureus.