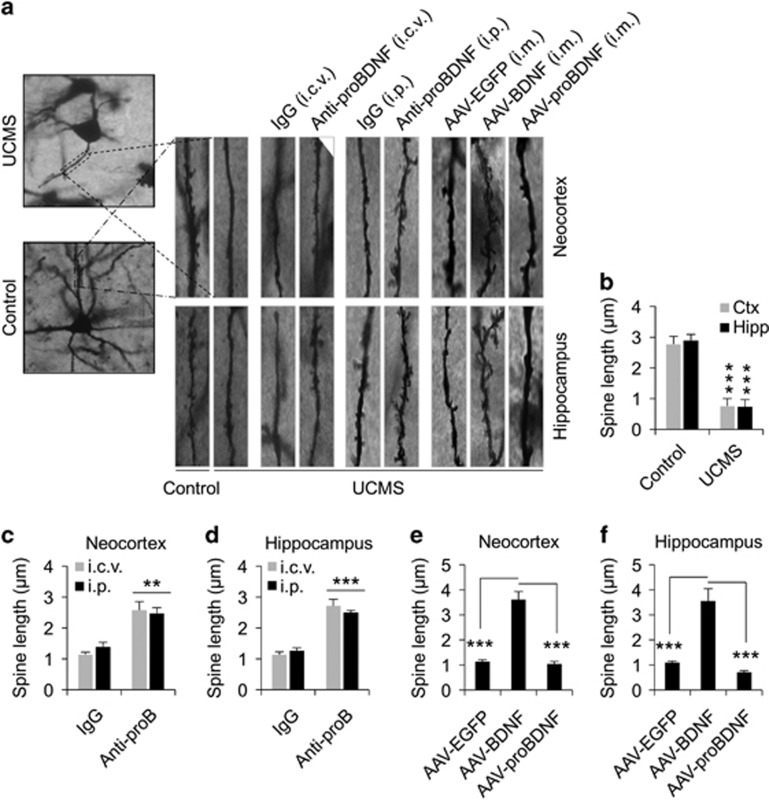
Figure 5.
Anti-proBDNF antibody improved but AAV-proBDNF did not exacerbate the UCMS-induced reductions in the dendritic spine length in rats. (a) Representative images of dendritic spines in cortical and hippocampal neurons were compared among control, UCMS, UCMS treated with normal sheep IgG and anti-proBDNF (i.c.v.), UCMS with IgG and anti-proBDNF (i.p.), as well as UCMS with AAV-EGFP, AAV-BDNF, and AAV-proBDNF (i.m.). (b–f) The spine lengths of cortical and hippocampal neurons were quantified and compared between/among control and UCMS rats (b), IgG and anti-proBDNF (i.c.v. or i.p.) injected UCMS rats (c, d), and AAV-EGFP, AAV-BDNF, and AAV-proBDNF (i.m.) injected UCMS rats (e, f). UCMS, unpredictable chronic mild stress; i.c.v., intraventricular; i.p., intraperitoneal; i.m., intramuscular; AAV, adeno-associated virus; Ctx, neocortex; Hipp, hippocampus; n=6–11 in each group, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001 (b–d, Student's t-test; e, f, one-way ANOVA). All data are presented as mean±SEM.