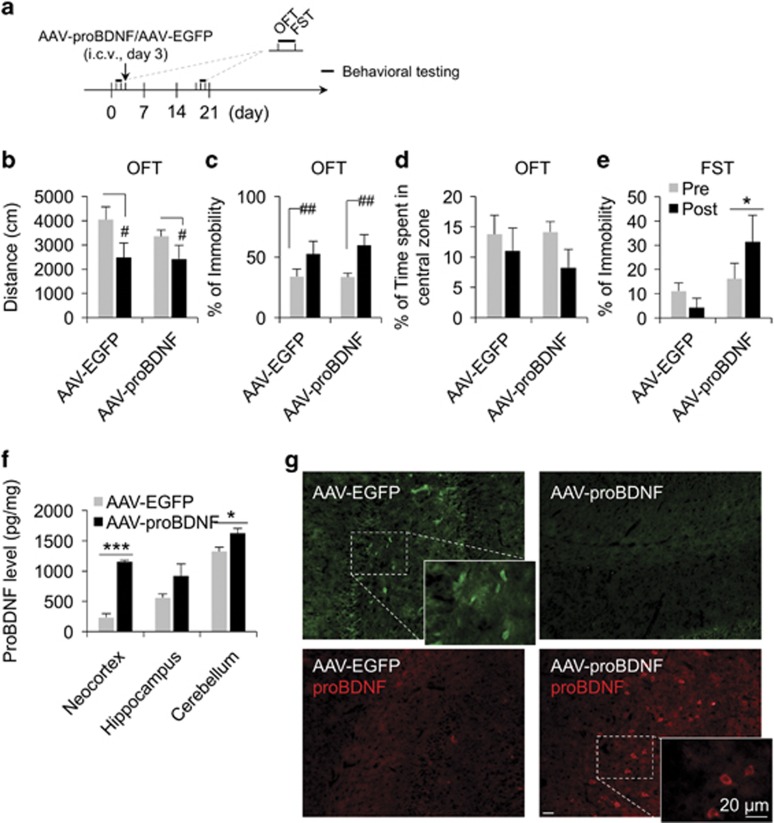
Figure 6.
Overexpression of proBDNF in the brain increased depression-like behavior but not anxiety-like behavior in naive rats. (a) Timeline of injection of AAV vector and behavioral testing. (b–e) The travel distances (b), percentage of immobility (c), and percentage of time spent in central zone (d) in the open field test, and the percentage of immobility in the forced swimming test (e) were compared at baseline (before injection) and after i.c.v. injection of AAV-EGFP or AAV-proBDNF (after injection). (f) The expression level of proBDNF in the neocortex, hippocampus, or cerebellum was detected by ELISA assay and compared between rats that received i.c.v. injection of AAV-EGFP or AAV-proBDNF. (g) The expression level of EGFP (direct imaging) or proBDNF (immunostaining using a specific antibody) in brain sections was compared between rats that received i.c.v. injection of AAV-EGFP or AAV-proBDNF; n=6 in each group; scale bar, 20 μm. OFT, open field test; i.c.v., intraventricular; FST, forced swimming test; *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 (proBDNF factor); #p<0.05, ##p<0.01 (injection factor). (b–e, two-way ANOVA; f, Student's t-test). All data are presented as mean±SEM.