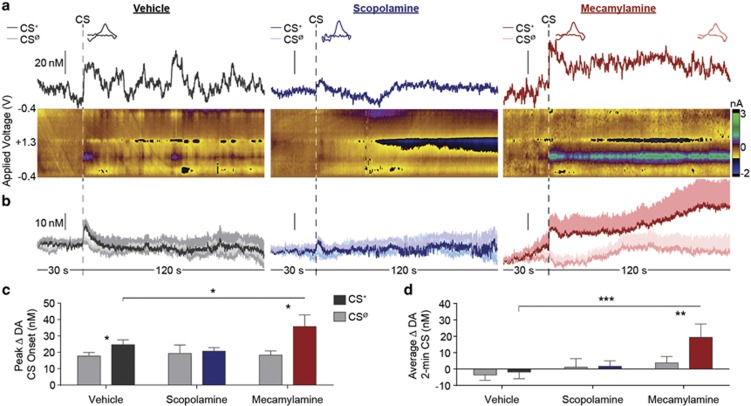
Figure 3.
Effect of nucleus accumbens muscarinic and nicotinic acetylcholine receptor blockade on cue-evoked dopamine signaling during Pavlovian-to-instrumental transfer. (a) Representative example, single-trial, FSCV data 30 s before and during the entire 2-min CS+, during the PIT test following the unilateral infusion of ASCF-vehicle (left), scopolamine (10 μg); (middle), or mecamylamine (10 μg); (right) into the NAc recording zone. Upper plot depicts the dopamine concentration vs time trace. Inset, cyclic voltammograms identifying the detected current as dopamine, taken from within the first 30 s following CS+ onset. Right inset of mecamylamine condition, average of CVs taken at 1-s intervals for the duration of the CS+ (shading shows SEM), confirming detection of sustained dopamine throughout the CS+. Color plots in the lower panels show corresponding background-subtracted cyclic voltammograms as a function of the applied voltage vs time. (b) Average (across trials of the same type and across subjects) dopamine concentration vs time trace change 30 s prior to and during the entire 2-min CS+ or CSØ period. Shading reflects +1 between-subjects SEM. (c) Peak dopamine concentration change in the 30-s period following CS+ or CSØ onset, averaged across trials. (d) Average dopamine concentration change during 2-min CS+ or CSØ period. n=10. Error bars represent±1 SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.