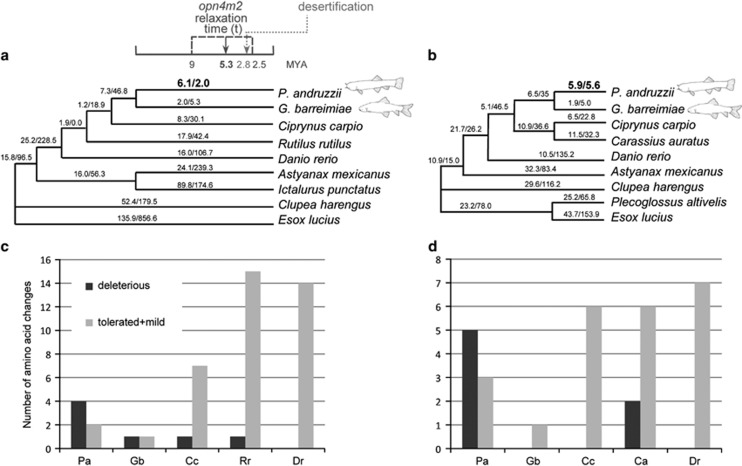
Figure 1.
The two species trees used for CODEML analyses of (a) melanopsin (opn4m2) and (b) rhodopsin (rho) genes. Branch lengths are not drawn to scale. The two numbers shown along each branch are the maximum likelihood estimates of the number of nonsynonymous and synonymous substitutions (N*dN and S*dS) along that branch (CODEML, free ratio model). Dates indicated with the dark gray arrow and dashed lines are inferred from the molecular genetic evidence of this study (opn4m2 relaxation time), whereas for the shift in climatic condition (desertification) we referred to deMenocal (1995). Melanopsin (c) and rhodopsin (d) species-specific amino acid changes are more likely to be deleterious in P. andruzzii (Pa) compared with changes in other cyprinid species (Ca, Carassius auratus; Cc, Ciprynus carpio; Dr, Danio rerio; Gb, Garra barreimiae; Pa, Phreatichthys andruzzii; Rr, Rutilus rutilus).