Fig. 5.
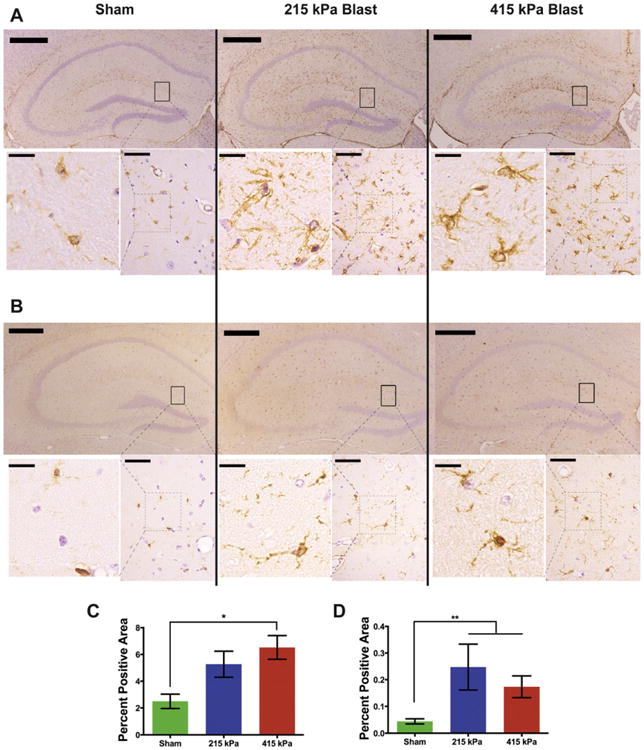
Primary blast loading caused reactive astrogliosis in the hippocampus. Staining for GFAP (A, C) and Iba1 (B, D) in the hippocampus increased subsequent to injury (GFAP: p = 0.01, Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn's post-hoc; Iba1: p < 0.01, Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn's posthoc). However, there was no significant difference in the increase between the two injured groups. n = 6, 7, 7 animals in the sham, 215 kPa and 415 kPa groups, respectively. Top panels for each: low magnification (5×) images of the hippocampus. Scale bars: 500 μm. Bottom panels for each (right hand side): higher magnification (63×) images of boxed regions in the low magnification images. Scale bars:50 μm. Bottom panels for each (left hand side): cropped images of the boxed regions in right hand side images. The area of the box is the same in all the images. Scale bars: 50 μm. *p < 0.05 posthoc in all.
