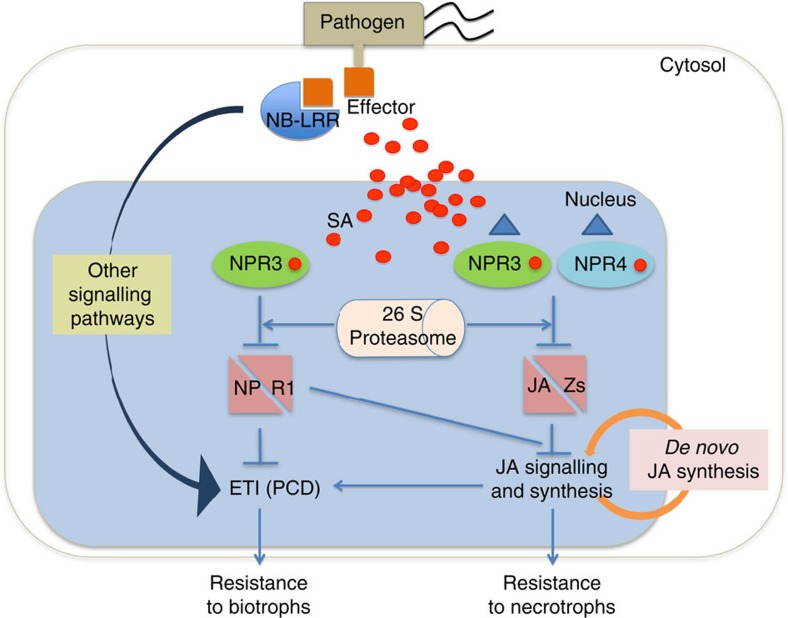
Figure 6. Working model of the interplay between SA and JA during ETI.
Activation of an NB-LRR immune receptor in plants by a pathogen effector leads to induction of multiple signalling pathways. A major event of the induction is the accumulation of SA at the infection site. At the high level of SA, NPR3 can interact with its substrate NPR1 to remove its repression on ETI and on crosstalk inhibition of the JA signalling pathway. Both NPR3 and NPR4 can also interact with JAZ proteins in an SA-enhanced manner leading to the degradation of JAZs. This results in activation of de novo JA synthesis of JA and amplification of the JA signalling through the canonical pathway. Activation of both SA- and JA-signalling pathways during ETI enables plants to use this PCD-associated defence strategy against biotrophic pathogens without making them vulnerable to necrotrophic pathogens. The blue triangle shape in the graph represents an unknown signal that may affect the degradation of JAZ1 through NPR3 and NPR4.