Figure 3. Enrichment of rare de novo CNVs and biallelic point mutations in individuals with ASD.
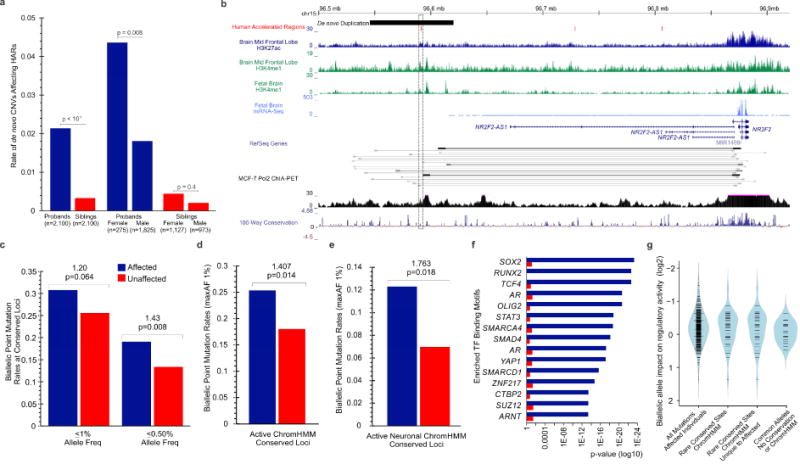
a) Excess of affected individuals with de novo CNVs affecting HARs. b) Intergenic de novo duplication approximately 250kb upstream of NR2F2 with existing ChIA-PET data indicating direct interaction between HAR and gene promoter. c) Excess biallelic mutations arising from the rarest alleles, including d) conserved loci within active regulatory elements (maxAF<1%) and within e) active neural regulatory elements. Transcription factor binding enrichment for target and associated genes of rare biallelic mutations (maxAF<1%) in f) affected and unaffected individuals. g) Increased impact of rare biallelic mutations in affected individuals at conserved sites using MPRA assay in primary mouse neurospheres. See also Figure S3 and Tables S5, S6, S7.
