Fig. 2.
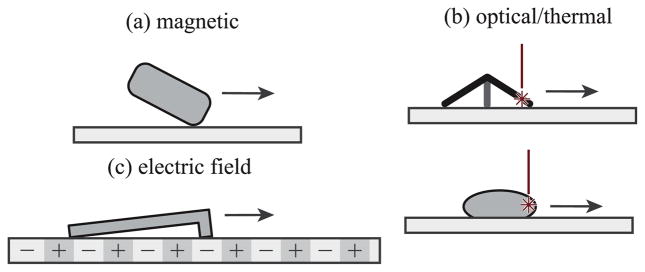
Some existing off-board approaches to mobile microrobot actuation and control in 2D. (a) Magnetically driven crawling robots include the Mag-μBot [33], the Mag-Mite magnetic crawling microrobot [59], the magnetic microtransporter [60], rolling magnetic microrobot [61], the diamagnetically-levitating mm-scale robot [62], the self-assembled surface swimmer [63], and the magnetic thin-film microrobot [64]. (b) Thermally driven microrobots include the laser-activated crawling microrobot [31], microlight sailboat [43], and the optically controlled bubble microrobot [39]. (c) Electrically driven microrobots include the electrostatic scratch-drive microrobot [65] and the electrostatic microbiorobot [60]. Other microrobots which operate in 2D include the piezoelectric-magnetic microrobot MagPieR [66] and the electrowetting droplet microrobot [67].