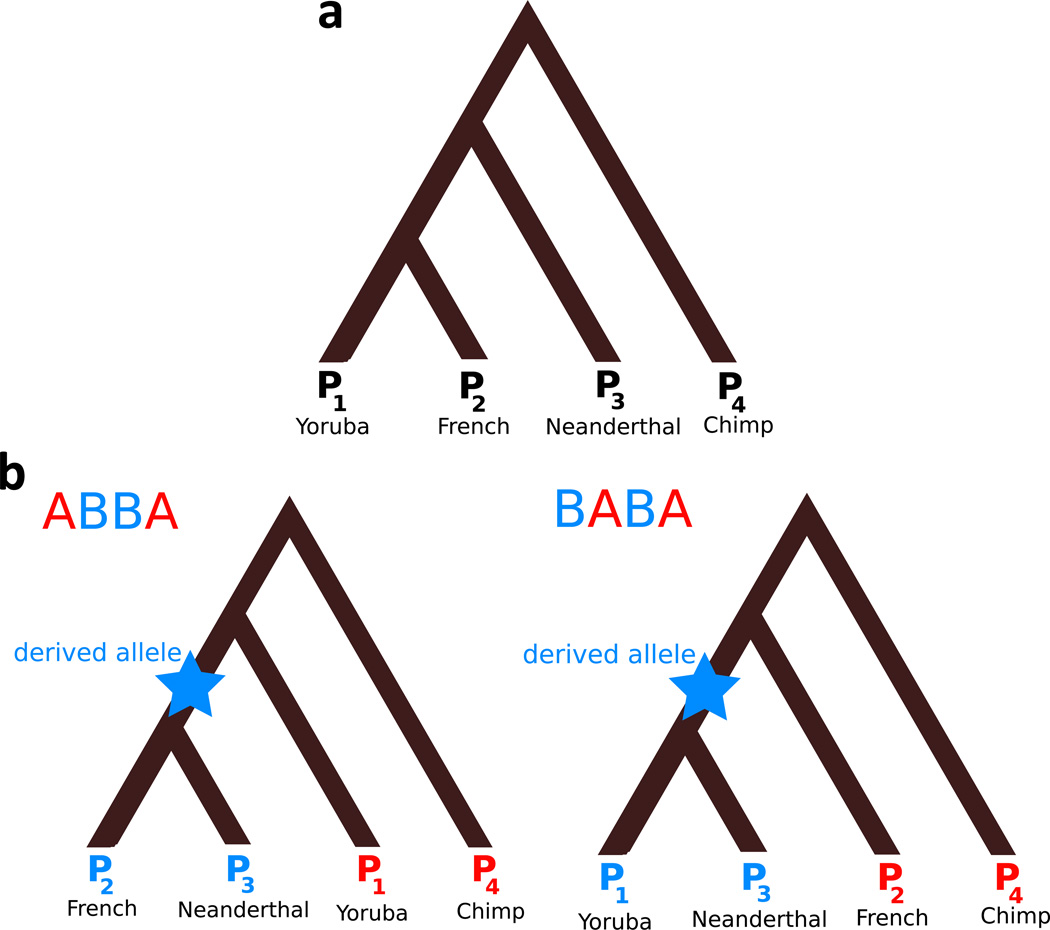
Figure 5.
Explanation of D statistic (Green et al. 2010; Durand et al. 2011). Individuals are numbered according to the D-statistic notation: D(P1, P2, P3, P4) and examples of individuals that could be used to yield a positive D-statistic result when testing for Neanderthal ancestry are given (D would be negative in this case if there had been gene flow between the Yoruban and Neanderthal instead). a: genome-wide tree relating the four individuals, based on prior knowledge. b: trees at ABBA and BABA sites used to compute D. In both, blue is used to represent a derived allele (does not match chimpanzee); red represents an ancestral allele (matches chimpanzee). To calculate D on sequence data, the number of sites with the topology of the left tree is NABBA and the number of sites with the topology of the right tree is NBABA. Then .