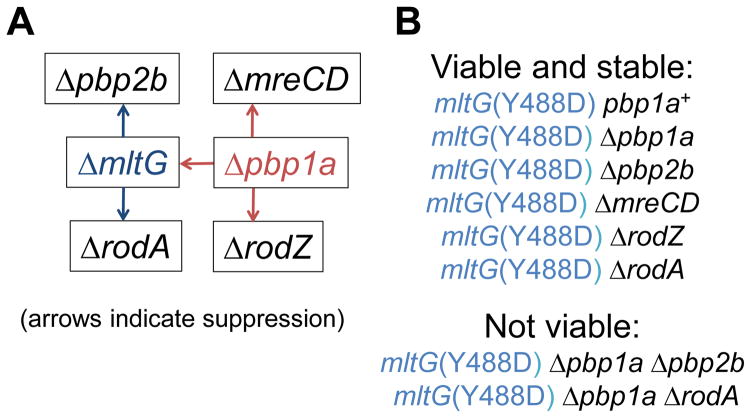
Fig. 4.
Summary of Δpbp1a synthetic-viable suppression patterns and viable and inviable mutation combinations with the mltG(Y488D) mutation. (A) Red arrows indicate direct suppression of ΔmltG, ΔmreCD, and ΔrodZ mutations by the Δpbp1a deletion. Blue arrows indicate suppression of Δpbp2b and ΔrodA mutation by the combination of ΔmltG Δpbp1a mutations (Tables 2 and 3). (B) mltG(Y488D) suppresses the requirement for each component of the peripheral PG synthesis machine, including essential proteins PBP2B, MreCD, RodZ, and RodA, as well as combinations of mutations that were tested in this study (Tables 2 and 3). Neither the mltG(Y488D) Δpbp1a Δpbp2b nor mltG(Y488D) Δpbp1a ΔrodA mutant could be constructed by multiple strategies. Construction of strains is described in Supplemental experimental procedures and Table S1. See text for additional details.