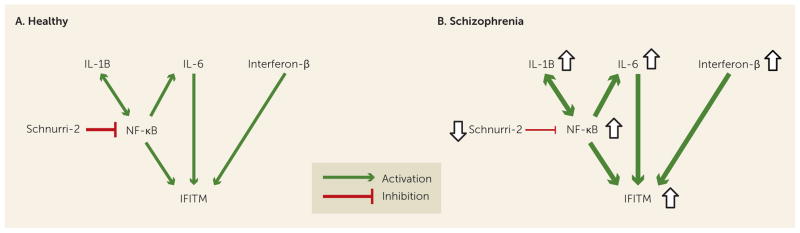
FIGURE 1. Schematic Illustration of the Relationships Among Immune Markers in the Healthy State and in Schizophreni a.
aPanel A illustrates factors regulating IFITM expression in the healthy state. Interleukin 6 (IL-6) and interferon-β induce IFITM expression. The transcriptional regulator nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) plays a central role in regulating the expression of many immune-related genes, including IL-1B and IL-6, is itself regulated by immune-related cytokines (e.g., IL-1B), and increases expression of IFITM. The NF-κB site-binding protein Schnurri-2 inhibits NF-κB function. Panel Billustrates the molecular cascade of immune activation in schizophrenia. The markedly higher mRNA levels for IL-1B, IL-6, interferon-β, and NF-κB, and lower mRNA levels for Schnurri-2, in the prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia subjects all converge to increase levels of IFITM mRNAs.