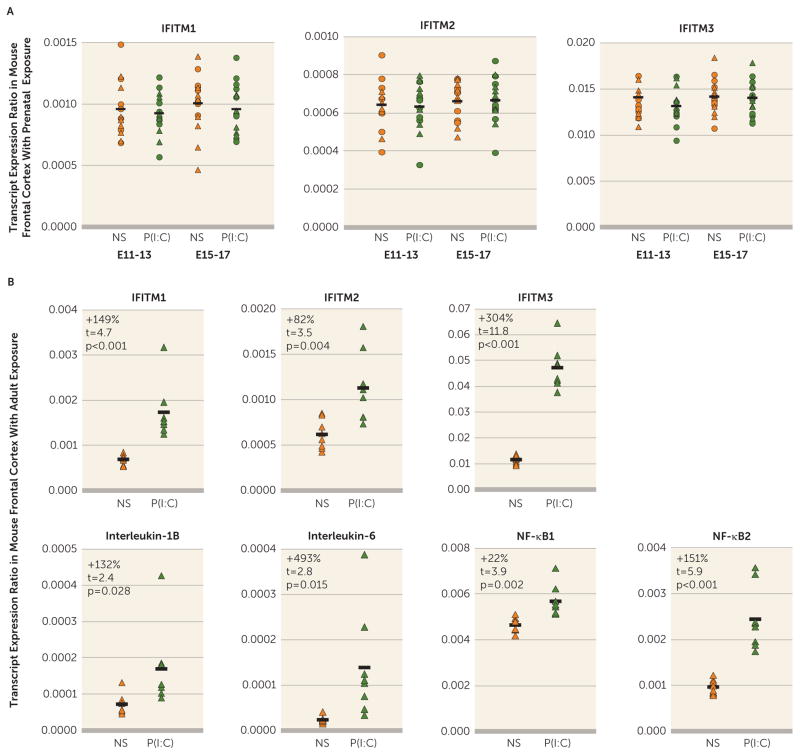
FIGURE 4. Transcript Levels for Immune System-Related Markers in the Frontal Cortex of Adult Mice Exposed Either Prenatally or in Adulthood to Immune Stimulationa.
aPanel A illustrates transcript levels for three variants of IFITM (IFITM1, IFITM2, IFITM3) in the frontal cortex of adult offspring (circles indicate males, triangles indicate females) of pregnant mice exposed to either normal saline (NS) or poly(I:C) [P(I:C)] daily for 3 days of gestation (embryonic day 11–13 [E11–13]: N=7 males and 7 females per condition; embryonic day 15–17 [E15–17]: N=8 males and 8 females per condition). Black bars indicate mean mRNA levels of both sexes combined for each condition. IFITM mRNA levels did not differ in adult offspring (i.e., male alone, female alone, or sexes combined) exposed prenatally to maternal immune activation in either middle (E11–13) or late (E15–17) gestation. In panel B, transcript levels for immune-related markers including different variants of IFITM, cytokines, and nuclear factor (NF)-κB were markedly higher in the frontal cortex of adult female mice exposed to poly(I:C) (N=8) relative to mice exposed to normal saline (N=8) daily for 3 days (df=14 in all analyses).