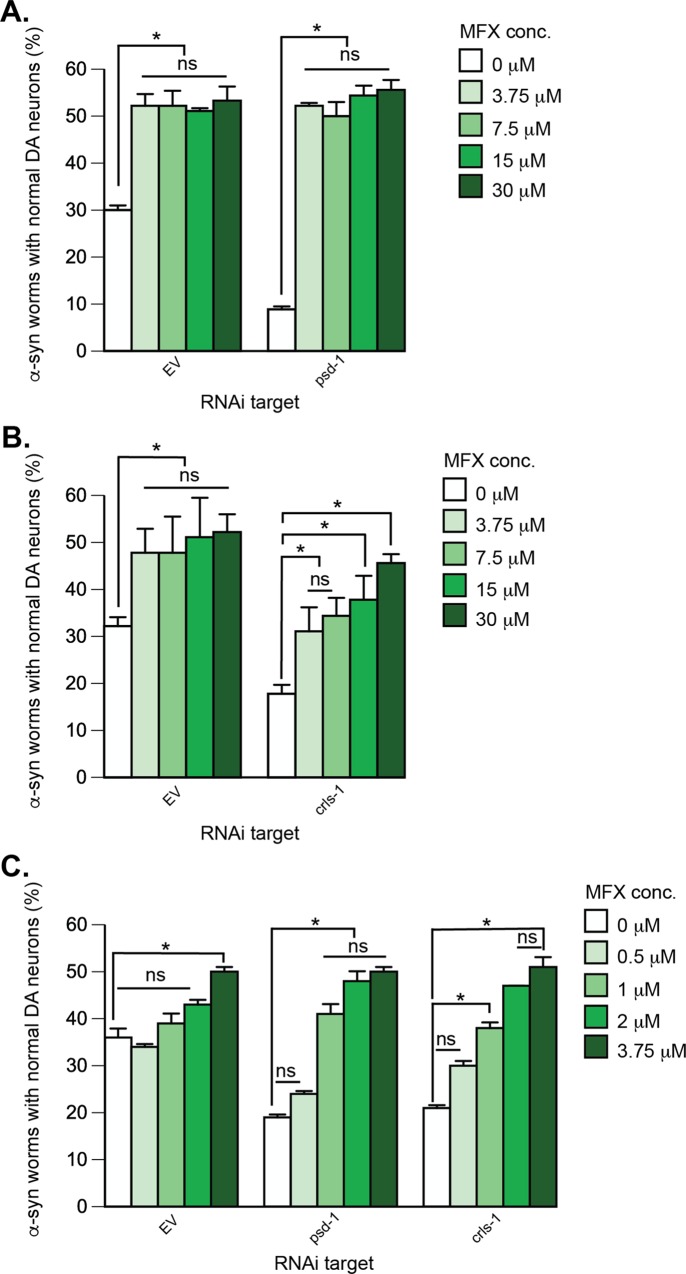
Fig 4. α-syn-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration in C. elegans is rescued by MFX.
Treatment of α-syn-expressing dopaminergic neurons with psd-1 or crls-1 RNAi, which causes enhanced neurodegeneration compared to α-syn alone, is also rescued by MFX (A—C). Graphical representation of C. elegans strain UA196 [sid-1(pk3321); Pdat-1::α-syn, Pdat-1::GFP; Pdat-1::sid-1, Pmyo-2::mCherry] following psd-1 (A, C) or crls-1 (B, C) knockdown. For RNAi experimental conditions, synchronized C. elegans were analyzed at day 7 post-hatching. RNAi bacteria, which do not express an RNAi clone (EV), were used as a negative control. A worm was scored as normal when it had a full complement of six anterior dopaminergic neurons. Data are reported as the mean ± SD, n = 90 worms. *p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA. (A) C. elegans fed with EV or psd-1 dsRNA were treated with MFX (0, 3.75, 7.5, 15, 30 μM dissolved in 0.1% v/v DMSO). (B) The same MFX concentrations were analyzed following dopaminergic neuron-specific EV or crls-1 knockdown. (C) C. elegans fed with EV, psd-1, or crls-1 dsRNA were treated with MFX (0, 0.5, 1, 2, 3.75 μM dissolved in 0.1% v/v DMSO).