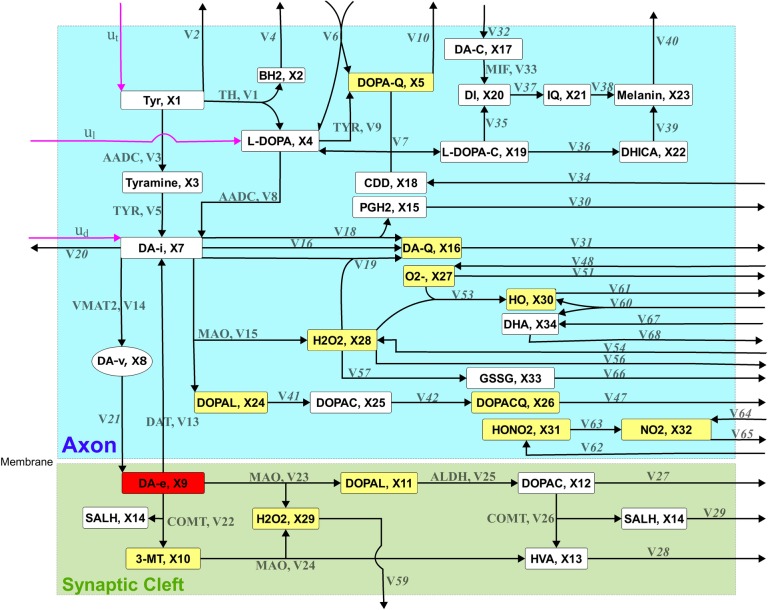
Fig 4. Schematic network diagram of the presynaptic dopamine metabolic pathway.
The extracellular dopamine (DA-e) concentration of 400 (relative unit) under a healthy state (HS) was first obtained from the kinetic model. The concentrations of the metabolites for various deficiencies of VMAT2 and TH are listed in supporting information (S1 Table). DA-e is the therapeutic objective: the dopamine level as close to its healthy level as possible that the identified enzyme targets can achieve. Other metabolites of interest included toxic species, reactive oxygen species (ROS), and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). Toxic species considered in this model were dopaquinone (DOPA-Q), 3-methoxytyramine (3-MT), 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (DOPAL), extracellular DOPAL (DOPAL-e), 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate quinone (DOPAC-Q), and dopamine quinone (DA-Q). ROS included superoxide (O2−), intracellular hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), extracellular H2O2 (H2O2-e), and hydroxyl radical (HO), whereas RNS included peroxynitrite (HO–NO2) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). In this study, the toxic species, ROS, and RNS were considered the objectives for evaluating adverse effects.