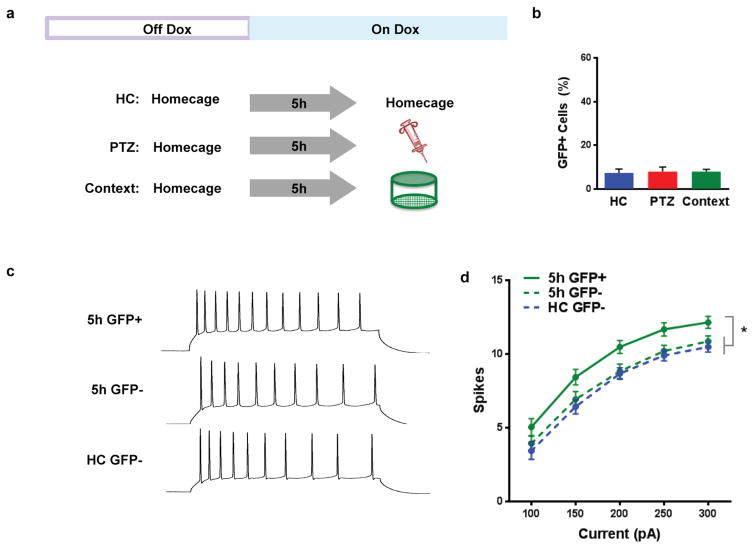
Extended Data Figure 3. Five hours after exploration of a context, GFP expression is shut off by doxycycline and excitability is increased.
a, Experimental design. Mice were removed from low levels of dox (40mg/kg) and given regular chow for 3 days to open up the GFP tagging window. After receiving administration of high dox (1g/kg) for 5h, mice were injected with 30mg/kg of pentylenetetrazole (PTZ), exposed to a novel context or left in their homecage. An hour later, mice were transcardially perfused and processed for GFP expression. b, There was no difference in GFP expression between the 3 groups (one-way ANOVA, F2,5 = 0.04, n.s., n=3,3,2), demonstrating that 5h was enough time for dox (1g/kg) to suppress expression of new GFP. c, To test excitability learning-related excitability changes, mice explored a novel context and then were administered high dox to shut off new GFP. Five hours later, mice were sacrificed for in vitro slice physiology. d, A two-way repeated measures ANOVA (group × current step) had a significant main effect of group (F2,68 = 4.20, p<0.05, n=21,29,21). 5h GFP+ group had more spikes than the 5h GFP- group (t68 = 2.31, p<0.05) and HC GFP- (t68 = 2.72, p<0.05). There was no difference between 5h GFP- and HC GFP- groups (t68 = 0.61, n.s.). Results show mean +/− sem.