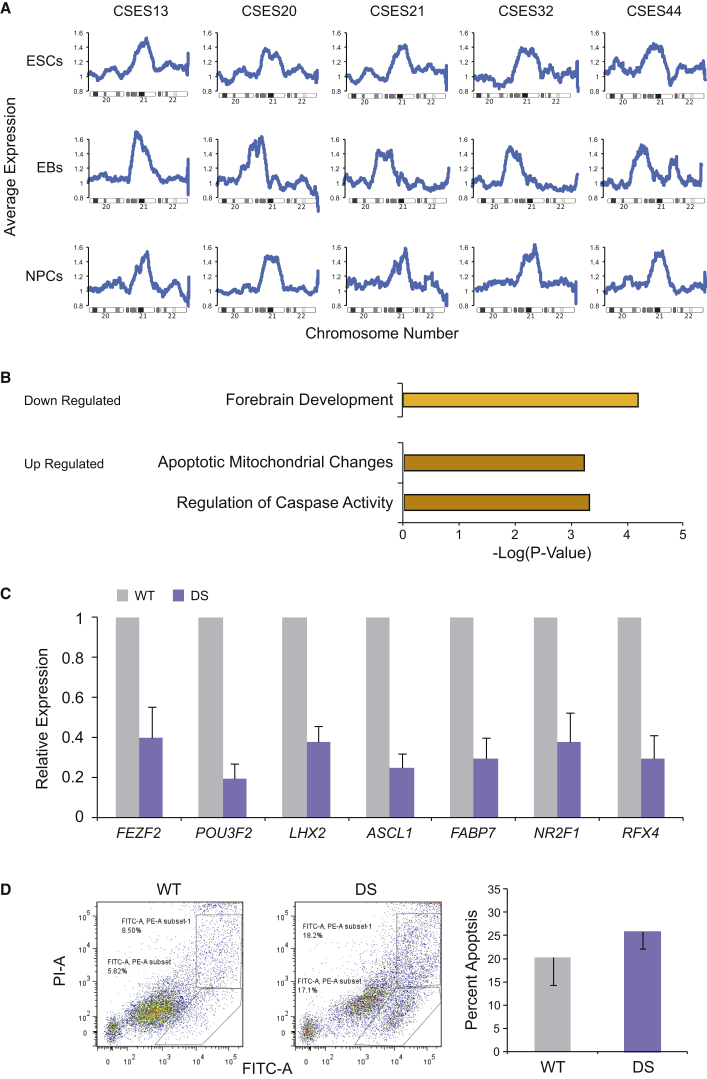
Figure 2.
Molecular Characterization of DS-NPCs
All five DS cell lines were differentiated into EBs and NPCs.
(A) Gene-expression analysis of undifferentiated ESCs, EBs, and NPCs of all five DS cell lines show a 1.5-fold higher expression of chromosome 21 compared with chromosomes 20 and 22 as seen by the moving average plot.
(B) Functional annotation clustering, based on three arrays of WT cells and five arrays of DS cells, shows downregulation of forebrain development genes and upregulation of apoptosis-related genes in DS-NPCs; only genes that were up- or downregulated by 2-fold were analyzed.
(C) DS-NPCs show downregulation of several key neuro-developmental genes. For WT, three microarrays of three different cell lines were used, for DS, five microarrays of the five independent DS cell lines were used. Error bars represent SEM.
(D) Flow cytometry analysis performed on five DS-NPC lines and three WT-NPC lines exhibits more apoptotic cells in DS cells by the summation of annexin V+(FITC+)/PI− and annexin V+(FITC+)/PI+ cell populations. Shown are representative results from DS-NPCs (middle panel) and WT-NPCs (left panel). Bar graph represents the average summation of annexin V+/PI− and annexin V+/PI+ populations as percent apoptosis in DS-NPCs and WT-NPCs of all lines used. Error bars represent SEM.