Figure 10. EGFP in the facial motor nucleus resulting from facial nerve axotomy.
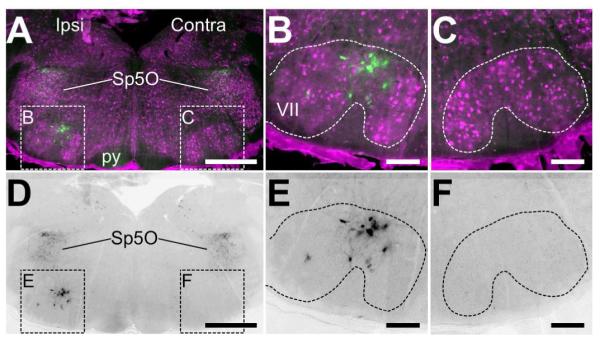
A) and D) Low-resolution images of the hindbrain showing the facial motor nuclei ispi- and contra-lateral to the site of facial nerve axotomy. In (A), NeuN immunostaining (magenta) shows the anatomical position of the facial motor nucleus (VII). Only on the ipsilateral side are there cells intensely labeled for EGFP in VII, whereas labeled cells can be found in the spinal nucleus of the trigeminal oral part (Sp5O) and diffuse staining in the pyramid of the corticospinal tract (py). In (D), only the EGFP immunoreactivity of the image in (A). Scale bars = 200μm. B) and E) High-resolution insets of the ipsilateral VII containing EGFP-positive cells defined in (A) and (D). The cells are large in size and have a neural morphology with processes. Scale bars = 50μm. C) and F) High-resolution insets of the contralateral VII defined in (A) and (D). No EGFP immunoreactivity is detected. Scale bars = 50μm.
