Figure 5.
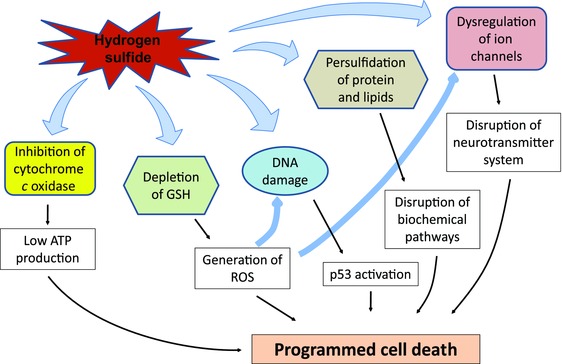
Potential mechanisms of H2S‐induced cytotoxicity. Hydrogen sulfide inhibits cytochrome c oxidase in mitochondria, leading to low ATP production. H2S also disrupts calcium homeostasis, leading to high intracellular calcium. Depletion of reduced glutathione leads to generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). H2S induces DNA damage, persulfidation of protein and lipids, and dysregulation of ion channels, which are further aggravated by excessive intracellular levels of ROS. Collectively, these H2S‐induced effects may lead to programmed cell death in neurons and glia.
