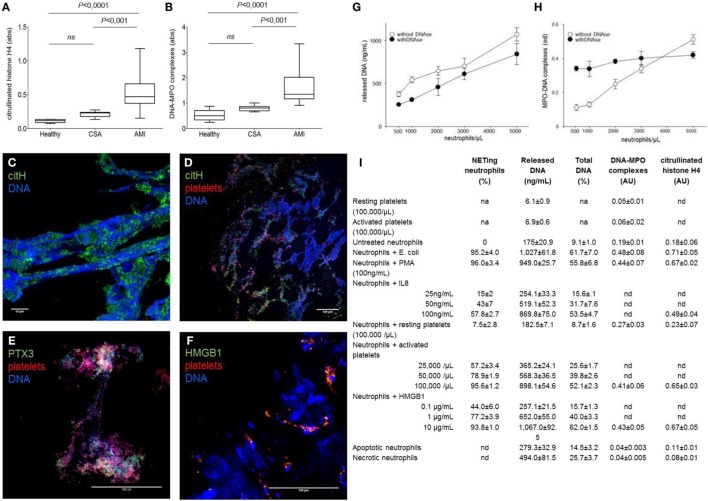
Figure 1.
NETs by-products are easily detected in the plasma of patients ongoing acute myocardial infarction and reflect the NETs that characterized coronary thrombi. (A–F) Coronary thrombi and plasma samples were obtained from 26 consecutive patients with STEMI underwent percutaneous intervention within 1–6 h from the onset of chest pain. NETs by-products were determined in plasma samples (anticoagulated with EDTA, venipuncture through a 19-gage butterfly needle) and processed within 15 min of sampling. Whole blood was centrifuged 15 min (320 g; 4°C), and retrieved plasma was further centrifuged (5 min at 100,000 g, 4°C) to eliminate any cellular debris. Obtained plasma was then aliquoted and frozen until de-determination of NETs by-products. All steps of samples preparation were performed in sterile conditions. (A,B) The amount of DNA–MPO complexes and the quantification of histone H4 citrullinated were assessed in the plasma samples of the same AMI patients in which were analyzed the composition of coronary thrombi, patients with chronic stable angina (CSA) candidates for coronary revascularization, and sex- and age-matched healthy donors. (C–F) Representative confocal analysis of coronary thrombi of AMI patients obtained during revascularization procedure. NETs were identified as DNA lattices with evident citrullination of histones (C,D) and by the presence of specific neutrophil proteins such as PTX3 (E). We consistently detected the presence of NETs in close proximity of platelets (D–F) that frequently express HMGB1 (F) [adapted from Maugeri et al. (5)]. (G,H) The use of DNAs impaired the sensitivity on NET determination: addition of DNase seems useful when low numbers of neutrophils are used. Freshly purified human neutrophils (0.5–5 × 106) of healthy donors were placed on poly-l-lysine-coated slides for 20 min at 37°C, then were challenged with PMA (100 ng/mL) for 20 min at 37°C. Then, treated or not with DNase I, after incubation plates were centrifuged 5 min (320 g; 4°C), supernatants were retrieved and further cleared (5 min at 100,000 g) and frozen until determination of NETs by-products and cell-free DNA as we previously described [adapted from Maugeri et al. (5)]. (I) Quantitative assays for NET formation. The results of a series of independent experiments carried out with cells of different donors are presented in this back-to-back comparison of different quantitative assays to estimate the degree of NET generation. Neutrophils were stimulated with a large panel of agonists to reproduce the environmental variability that occurs under physiological conditions. Quantitation of cell-free DNA is consistent with the degree of NET generation as estimated by direct microscopy visualization and MPO/DNA- or citrullinated histone-based techniques in this set of experiments, where purified neutrophils were employed [adapted from Maugeri et al. (5)].