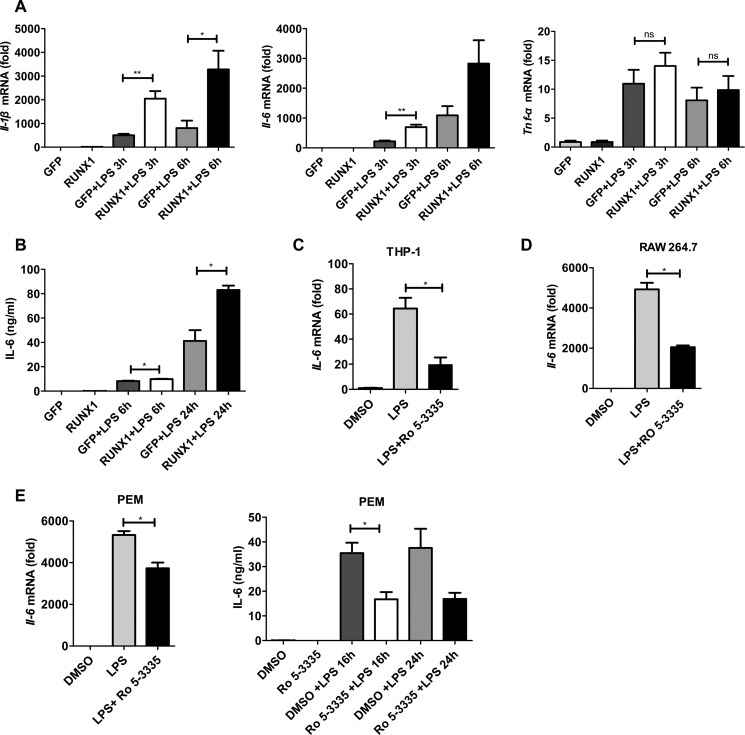
FIGURE 2.
Regulation of IL-6 and IL-1β production by RUNX1 overexpression or treatment with a RUNX1 inhibitor. A and B, RUNX1-GFP or a GFP vector control (6 μg) were co-transfected with pCL-10A1 (6 μg) into 293T cells. The retroviral supernatants were harvested and used to infect RAW264.7 cells, which was followed by FACS sorting of the GFP+ cells. These stable RAW264.7 cells that overexpressed RUNX1 or GFP were stimulated with 100 ng/ml of LPS for the indicated times. The Il-1β, Il-6, and Tnf-α mRNA levels were measured with RT-qPCR (A), and the IL-6 levels in the supernatants were determined with ELISA (B). The data are shown as the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. THP-1 cells (C), RAW 264.7 cells (D), and PEMs (E) were stimulated with LPS (100 or 1000 ng/ml) for 4 h in the absence or presence of the RUNX1 inhibitor, Ro 5-3335 (50 μm). IL-6 levels were measured by RT-qPCR or ELISA. The data are shown as the mean ± S.D. of a representative of three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.