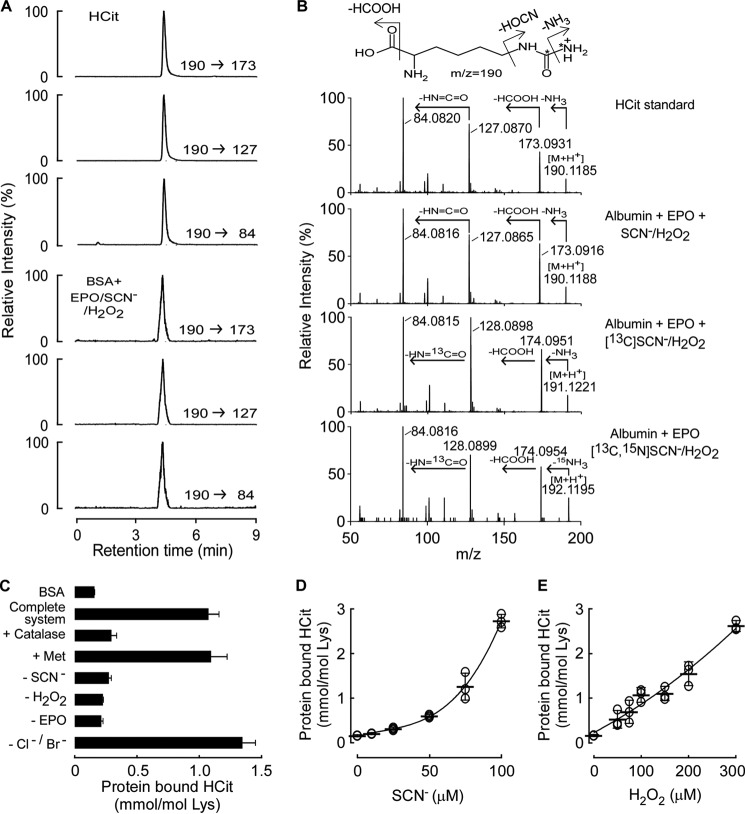
FIGURE 1.
Protein carbamylation is catalyzed by the EPO/SCN−/H2O2 system. A, extracted ion chromatograms in positive multiple reaction monitoring mode of HCit standard and the hydrolysate of BSA after reaction with EPO/SCN−/H2O2 with parent-to-daughter transitions, m/z 190 → 173, 190 → 127, and 190 → 84, respectively. B, MS/MS spectra in positive mode of HCit standard, and the HCit isotoplogue in the albumin hydrolysate after reaction with SCN−, [13C]SCN−, or [13C,15N]SCN− and H2O2 in the presence of EPO. The mass spectra were acquired by Triple TOF with positive information-dependent acquisition mode. C, reaction requirements and quantification of protein (BSA, 1 mg/ml) carbamylation by the EPO/SCN−/H2O2 system under physiological concentrations of halides (100 mm Cl−, 100 μm Br−, 100 μm SCN−), 100 μm H2O2, and 60 nm EPO with catalase (500 nm) and methionine (500 μm) as indicated. D and E, protein carbamylation occurs across physiological concentration ranges of SCN− and H2O2. The concentrations of H2O2 in D and SCN− in E are 300 and 100 μm, respectively. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. for two (C) independent experiments or scatter plots for individual experiments with mean ± S.D. indicated (D and E).