FIGURE 2.
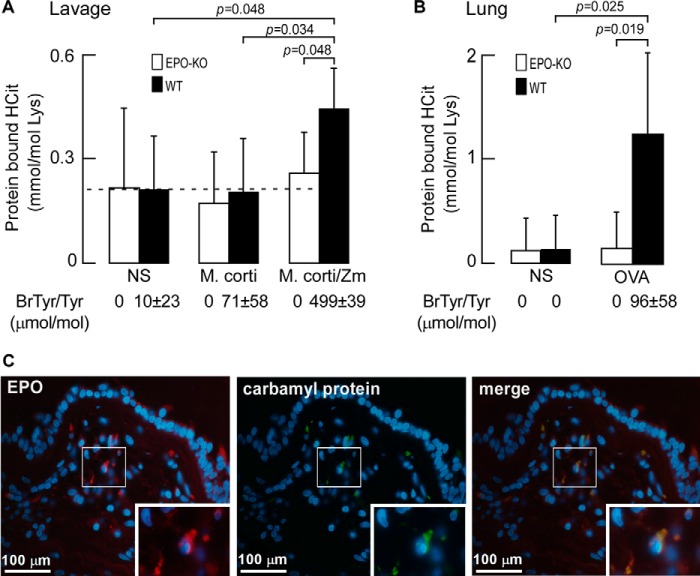
EPO is a catalytic source for carbamylation at sites of inflammation and within asthma airway specimens. A, abundance of protein-bound HCit recovered from peritoneal lavage supernatants of wild-type (WT) and EPO-deficient (EPO-KO) mice (n = 5 per group) presensitized to M. corti whole protein extract and then injected with normal saline (NS), M. corti antigen, or M. corti antigen with zymosan (M. corti/zymosan) as indicated after cell pellet removal. Abundance of protein-bound bromotyrosine (BrTyr) as an indicator of EPO-specific activity is listed. B, abundance of protein-bound HCit in homogenates of lung tissue after ovalbumin allergic asthma induction. Ovalbumin pre-sensitized wild-type (WT) and EPO-KO mice (n = 6 per group) 24 h after final challenge of either normal saline (NS) or OVA challenge. Data represent the mean ± S.D. for independent replicates (A and B). Protein-bound BrTyr levels as in A are indicated. C, representative fluorescence microscopy of a human asthma airway biopsy specimen identifies EPO and carbamyl protein localization. Sections were immunostained with either monoclonal antibodies to EPO (left panel) or carbamylated proteins (middle panel). The merged image (right panel) reveals co-localization of EPO and carbamyl proteins. Nuclei were stained with DAPI and insets are magnifications of the boxed sections. Protein-bound bromotyrosine level, expressed as BrTyr/Tyr (μmol/mol), was reported previously (20).