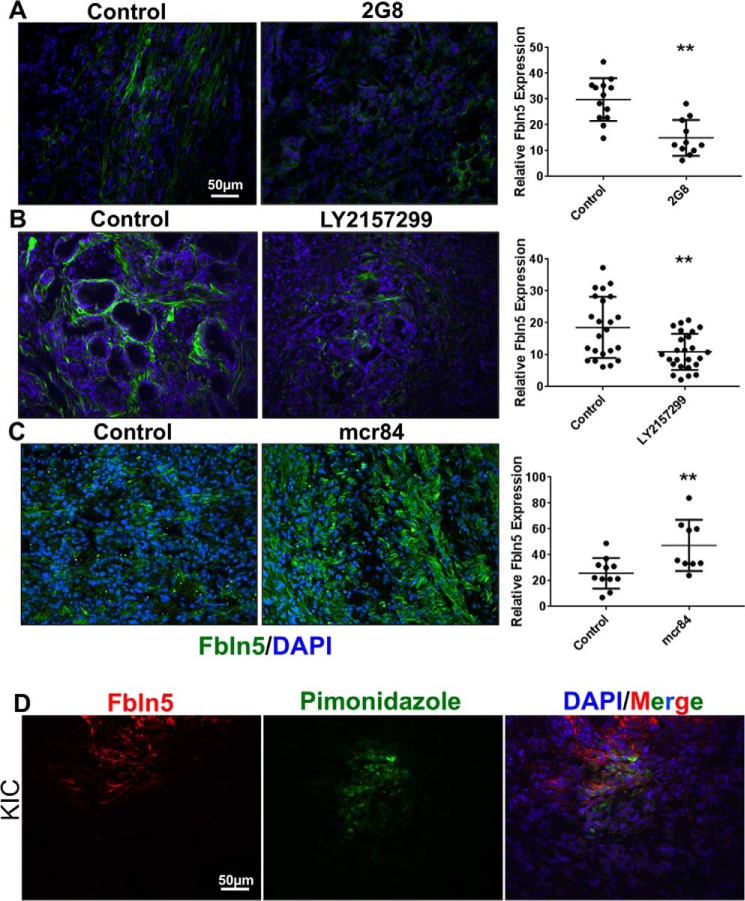
FIGURE 5.
Inhibition of TGF-β receptors reduces Fbln5 expression, whereas anti-VEGF therapy induces its expression in mouse PDA. A, frozen tumor sections from KPC mice treated with 2G8 at 30 mg/kg/week (n = 4) or left untreated (n = 4) and probed for Fbln5 by immunohistochemical staining. B, frozen tumor sections from KPC mice treated with 75 mg/kg LY2152799 twice daily (n = 4) or left untreated (n = 4) and probed for Fbln5. C, frozen tumor sections from KIC mice treated with 500 μg of mcr84 per week (n = 5) or left untreated (n = 4). D, mice were injected intravenously with 60 mg/kg of pimonidazole, which was allowed to circulate for 90 min before sacrificing the animals. Frozen tissue sections were interrogated with FITC-conjugated anti-pimonidazole primary antibody (green) and Fbln5 (red) (n = 3). A–D were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Results are shown as mean ± S.D. Fluorescent intensity was quantified per ×20 field image using NIS Elements software. The p values (*, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001; ***, p < 0.0001) were determined by Student's t test. Representative images from each treatment group are shown (n = 4–5/group, 8–12 pictures taken).