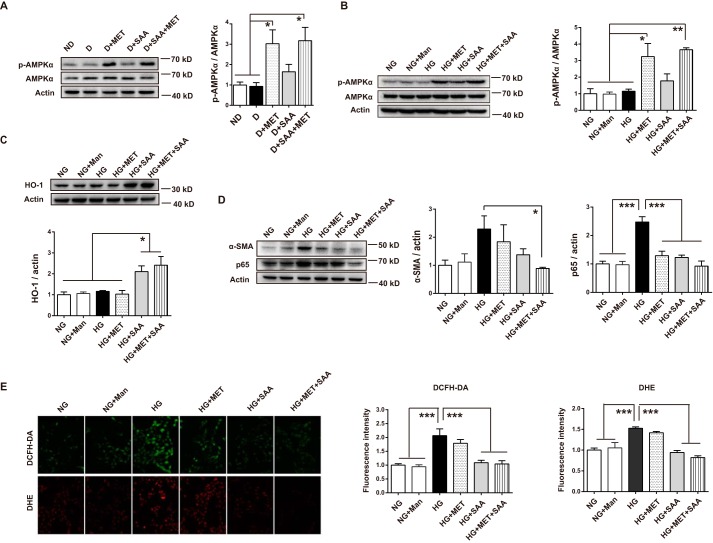
FIGURE 7.
Combination of SAA and MET inhibited HG-induced harmful effects in HK-2 cells through MET-mediated AMPK activation and SAA-induced HO-1 up-regulation. Expression of AMPK and p-AMPK in the diabetic kidney was analyzed by Western blotting, showing that MET activated AMPK (A) (n = 6 mice per group). HK-2 cells were treated with NG, Man, HG, HG + MET, HG + SAA, HG + MET + SAA for the indicated times. After a 12-h incubation, cell lysates were used to detect AMPK and p-AMPK expression by Western blotting, and the quantitation showed metformin-activated AMPK (B). After a 24-h incubation, HO-1 expression was analyzed by Western blotting, which showed that SAA induced HO-1 up-regulation (C). After a 48-h incubation, the α-SMA and p65 expression were analyzed by Western blotting, with their expression showing a trend toward further decreases under the SAA treatment in combination with MET (D). Similarly, HK-2 cells were treated with the above agents, or a combination for 48 h, and then evaluated by fluorescent microscopy after DHE and DCFH-DA treatments for 30 min (E, ×200). Results were mean ± S.E. (B–E, n = 3 independent experiments). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. NG, 5.5 mm normal glucose; HG, 25 mm high glucose; Man, 19.5 mm mannitol; MET, 2 mm metformin; SAA, 5 μm salvianolic acid A.