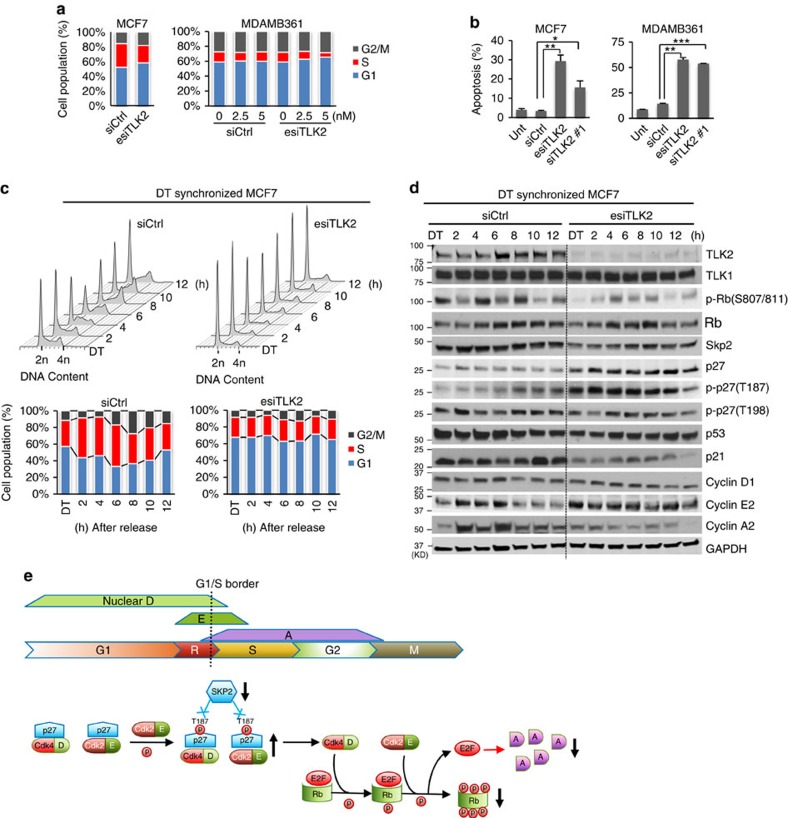
Figure 7. TLK2 inhibition results in impaired G1/S progression and induction of apoptosis in TLK2-amplified luminal breast cancer cells.
(a) Flow cytometry results showing cell cycle changes after TLK2 knockdown in asynchronized MCF7 and MDAMB361 cells. 10 nM siRNAs (for MCF7 cells) or indicated concentration of siRNAs (for MDAMB361 cells) were transfected for 72 h. Ctrl, Control. (b) Cell apoptosis assessed by Annexin V assay in asynchronized MCF7 and MDAMB361 cells following TLK2 knockdown via 20 nM esiTLK2 or siTLK2#1 transfection for 72 h. Error bars represent the s.d. of two replicate measurements per condition. P values are calculated based on t-test. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. (c) Cell cycle profile of synchronized MCF7 cells (by double thymidine block) after TLK2 inhibition. After TLK2 knockdown for 24 h, MCF7 cells were synchronized at the G1/S border using 2.5 mM double thymidine (DT), and then released. Cells were collected every 2 h after cell cycle release for up to 12 h, and analysed for DNA content using flow cytometry. (d) Western blot was done to examine the changes of key signalling molecules involved in G1/S cell cycle regulation using the cell lysates obtained from the same experiment as in 7c. ‘DT' indicates synchronized MCF7 cells by DT block. (e) A schematic of normal G1/S cell cycle signalling and alternations following TLK2 inhibition (black arrows). In normal cell cycle, the cyclin E level starts to increase in late G1 phase, and then collapses as the cells enter S phase53, followed by increased cyclin A expression54,55. Rb regulates G1/S transition by repressing the E2F transcription factors that control the expression of cyclin A. Once Rb is phosphorylated (that is, at S807/S811), it releases E2Fs, which will allow cells to enter S phase56,57. p27 inhibits the two G1 cyclin/cdk complexes, cyclin D/Cdk4 and cyclin E/Cdk2 (refs 36, 40), both of which are the key upstream kinases of Rb (ref. 37). During normal G1/S progression, the p27 proteins complexed with G1 cyclin/cdks were phosphorylated by the p27-free cyclin E/Cdk2 complexes at T187, which were then targeted for SKP2-mediated proteasome degradation58. D, Cyclin D. E, Cyclin E. A, Cyclin A. R, restriction point.