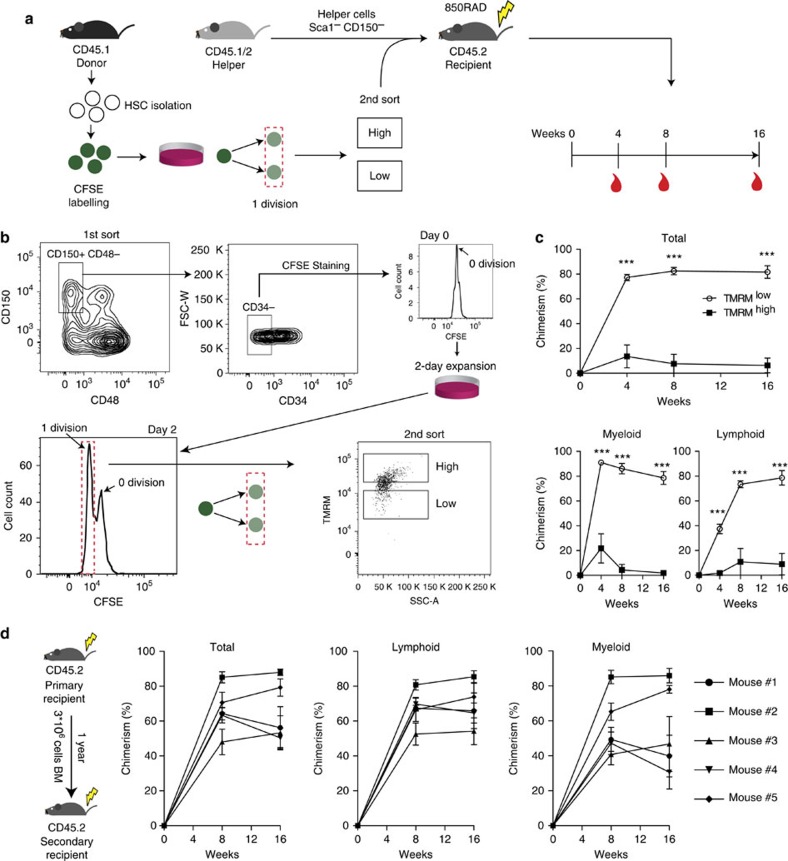
Figure 2. A low mitochondrial activity marks self-renewing HSCs.
(a) Experimental paradigm to assess mitochondrial activity as a discriminator of self-renewing from differentiating LT-HSCs in culture. Freshly isolated LT-HSCs were labelled with CFSE. At the end of the culture, cells that divided one time were further sorted into TMRMlow and TMRMhigh phenotypes and transplanted into lethally irradiated recipient mice together with helper cells. Blood reconstitution was assessed at 4, 8 and 16 weeks. (b) CFSE-labelled LT-HSCs were cultured under expansion conditions for 2 days and progeny that underwent one division were sorted into TMRMlow and TMRMhigh phenotypes, and 100 cells of each population (along with 2 million helper cells) were transplanted into lethally irradiated recipients. (c) The TMRMlow fraction of the first generation of daughter cells (that is, dividing one time) exhibited strikingly higher long-term multi-lineage blood reconstitution efficiency compared with TMRMhigh cells, providing evidence for self-renewing versus differentiating HSC divisions in culture (n=10 for each condition). Assessment of blood chimerism is shown for total blood (top panel) as well as the lymphoid and myeloid lineages (bottom panels; error bar: s.e.m.; t-student, ***P<0.001). (d) BM derived from each of the TMRMlow primary recipients (from c) was injected into four secondary recipient mice after 1 year of the primary transplant. Blood chimerism (average of four secondary recipients corresponding to each primary recipient) show long-term multi-lineage reconstitution in secondary transplants (error bar: s.e.m.).