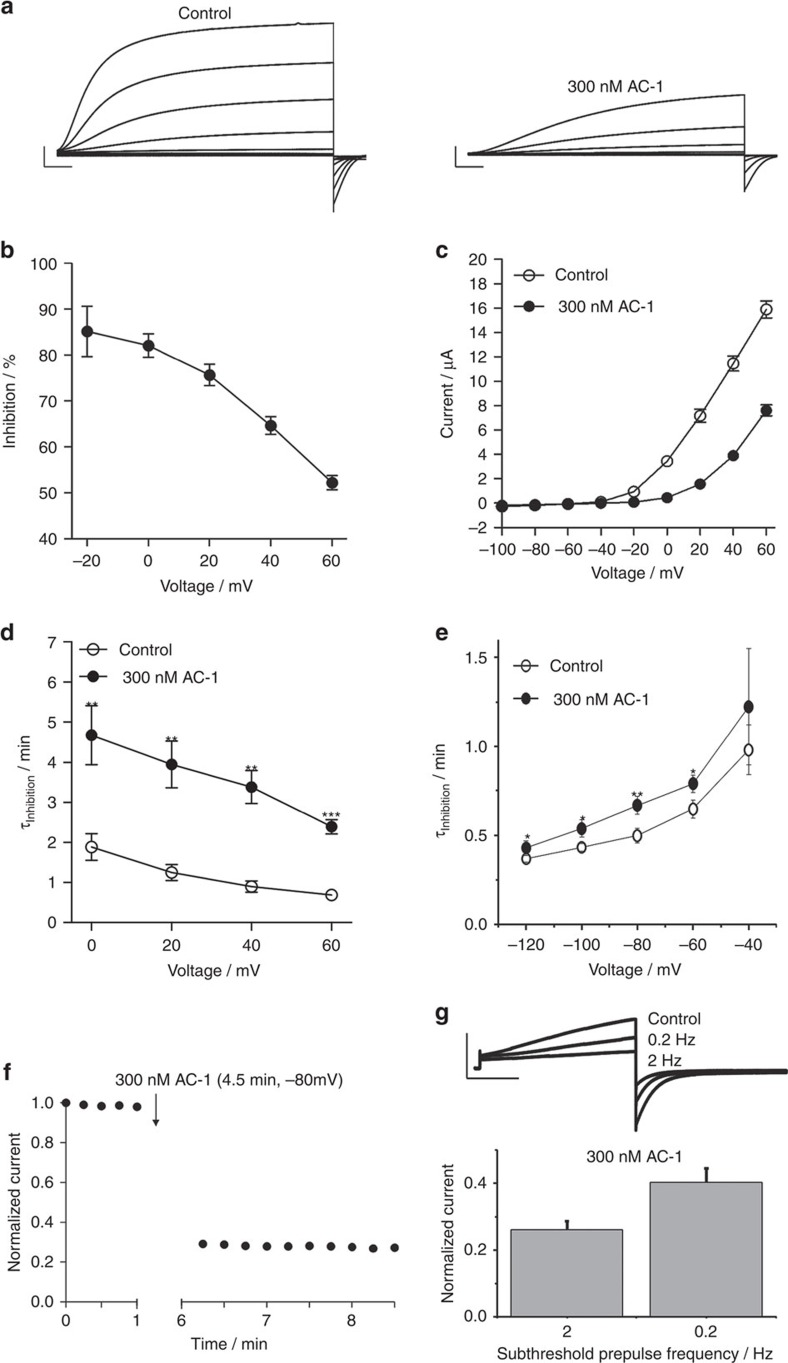
Figure 2. AC-1 alters activation kinetics and shifts voltage-dependence of activation.
(a) Example of Kv7.1/KCNE1 current traces recorded before and after application of 300 nM AC-1. Currents were elicited with 10 s pulses to potentials of −100 mV to +60 mV, applied in 20 mV increments from a holding potential of −80 mV. Tail currents were recorded at −120 mV (scale bars indicate 2 μA, 1 s). (b) Voltage dependence of AC-1 inhibition determined as percent change of current amplitude after application of 300 nM AC-1 (n=15,±s.e.m.). (c) Rates of current activation are slowed in the presence of 300 nM AC-1. Activation was described using a single exponential function. τactivation was plotted against the test potential (n=5, ±s.e.m.; Student's t-test; **P<0.01, ***P<0.001). (d) AC-1 shifts the voltage dependence of channel activation to more positive potentials. Macoscopic currents analysed at the end of test pulses and plotted against their respective test potential. (n=15, ±s.e.m.; Student's t-test). (e) Currents were activated by a 5 s depolarizing pulse to −20 mV. Tail currents were recorded at different test potentials ranging from −140 mV to −40 mV, applied in 20 mV increments. 300 nM AC-1 decreases the rate of current deactivation measured by fitting traces to a single exponential function to determine τdeactivation (n=7–9, ±s.e.m.; Student's t-test). (f) Channels were held in closed state during application of 300 nM AC-1 by clamping the oocyte to −80 mV for 4.5 min without pulsing. On re-initiation of pulsing to +40 mV, the inhibition of current magnitude was fully developed, indicating that AC-1 is able to access its binding site when channels are in the closed state. (g) Channels were activated by 5 sec 0 mV pulses to obtain a control value. Subsequently, 300 nM AC-1 were applied and channels were preconditioned for 1 min by 300 msec −40 mV -subthreshold prepulsing at 2 and 0.2 Hz (scale bars indicate 1 μA, 1 s). At the end of preconditioning channels were activated again by 5 s 0 mV pulses and the current amplitudes at the end of the activating pulse were normalized to the control value (n=8, ±s.e.m.; Student's t-test).