Figure 4.
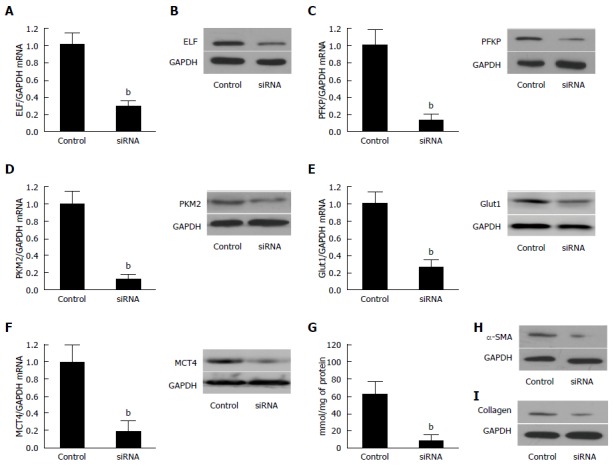
Silencing of Embryonic liver fordin in the activated hepatic stellate cells led to the inhibition of glycolysis. A: The ELF mRNA was reduced in the activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) transfected synthetic siRNA against ELF was assessed by real-time RT-PCR. P < 0.01 for the ELF siRNA versus the siRNA controls. GAPDH was used as the control; B: Western blot analysis confirmed that synthetic siRNA inhibited the ELF expression in the activated HSCs; C, D: The hepatic glycolytic enzymes, PFKP and PFKM2, expression of the mRNA and protein level decreased significantly after the ELF siRNA treatment (aP < 0.05 vs control). E, F: The hepatic glycolytic enzymes, Glut 1 and MCT 4, expression of the mRNA at the protein level decreased significantly after the ELF siRNA treatment (aP < 0.05 vs control). G: The intracellular lactate level decreased significantly after the ELF siRNA treatment (aP < 0.05 vs control); H, I: The main components of the extracellular matrix, α-SMA and collagen I, expression showed a remarkable decrease in the activated HSCs, and the HSC transfected synthetic siRNA against ELF.
